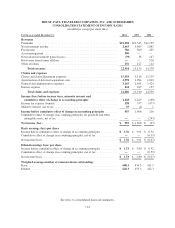
Travelers 2004 Annual Report Download - page 116
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 116 of the 2004 Travelers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
International and other claim liabilities result from a mix of coverages, currencies and jurisdictions/
countries. The common characteristic is the need to customize the analysis to the individual component, and the
inability to rely on data characterizations and reporting requirements in the U.S. statutory reporting framework.
Due to changes in the business mix for this line over time, the recently incurred claim liabilities are
relatively short term (due to both the products and the jurisdictions involved, e.g., the Republic of Ireland and the
United Kingdom), while the older liabilities include some from runoff operations that are extremely long tail
(e.g., U.S. excess liabilities reinsured through the London market, and several underwriting pools in runoff). The
speed of claim reporting and claim settlement is a function of the specific coverage provided, the jurisdiction, the
distribution system (e.g., underwriting pool versus direct), and the proximity of the insurance sale to the insured
hazard (e.g., insured and insurer located in different countries). In particular, liabilities arising from the
underwriting pools in runoff may result in significant reporting lags, settlement lags and claim complexity, due to
the need to coordinate with other pool members or co-insurers through a broker or lead-insurer for claim
settlement purposes.
International and other reserves are generally analyzed by program/pool, country and general coverage
category (e.g., U.S. Liability—excess of loss reinsurance, or General Liability – Municipalities – by country.)
The business is also generally split by direct versus assumed reinsurance for a given coverage/jurisdiction. Where
the underlying insured hazard is outside the United States, the underlying coverages are generally similar to those
described under the General Liability and Automobile discussion above, but under a different legal system.
Where the underlying hazard is within the U.S., the coverage involved is typically that of General Liability, but
on an excess or excess-of-loss reinsurance basis. Excess exposure requires the insured to “prove” not only claims
under the policy, but also the prior payment of claims reaching up to the excess policy’s attachment point.
Examples of common risk factors that can change and, thus, affect the required International and other
reserves (beyond those included in the general discussion section) include:
International and other risk factors
Changes in claim handling philosophies
Changes in policy provisions or court interpretation of such provision
New theories of liability
Trends in jury awards
Changes in the propensity to sue
Changes in statutes of limitations
Changes in the underlying court system
Distortions from losses resulting from large single accounts or single issues
Changes in tort law
Changes in claim adjuster office structure (causing distortions in the data)
International and other book of business risk factors
Changes in policy provisions (e.g., deductibles, policy limits, endorsements, “claims made” language)
Changes in underwriting standards
Product mix (e.g., size of account, industries insured, jurisdiction mix)
104