Rogers 2005 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2005 Rogers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
24 ROGERS 2005 ANNUAL REPORT . MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
will produce growth, the growth on a year-over-year percentage change basis is slowing compared to historical levels.
This deeper penetration drives an increased focus on customer satisfaction, the promotion of new data and voice
services and features and, primarily, customer retention. As discussed below, the Canadian Radio-television and
Telecommunications Commission (“CRTC”) is implementing Wireless Number Portability (“WNP”). As such, customer
satisfaction and retention will become even more critical in the future.
DE M A ND FO R S O P HI S TI C AT E D D A TA AP P L IC A TI O NS
The ongoing development of wireless data transmission technologies has led developers of wireless devices, such as
handsets and other hand-held devices, to develop more sophisticated wireless devices with increasingly advanced
capabilities, including access to e-mail and other corporate information technology platforms, news, sports, financial
information and services, shopping services, photos and video clips, and other functions. Wireless believes that the intro-
duction of such new applications will drive the growth for data transmission services. As a result, wireless providers will
likely continue to upgrade their digital networks to be able to offer the data transmission capabilities required by these
new applications.
MI G R AT I ON TO N EX T G E NE R A TI O N W IR E L ES S T E CHN O LO G Y
The ongoing development of wireless data transmission technologies and the increased demand for sophisticated
wireless services, especially data communications services, have led wireless providers to migrate towards the next
generation of digital voice and data networks. These networks are intended to provide wireless communications with
wireline quality sound, far higher data transmission speeds and streaming video capability. These networks are expected
to support a variety of increasingly advanced data applications, including broadband Internet access, multimedia
services and seamless access to corporate information systems, such as e-mail and purchasing systems.
DE V E LO P ME N T O F A D DI T IO N A L T EC H NO L O GI E S
The development of additional technologies and their use by consumers may accelerate the widespread adoption of
3G digital voice and data networks. One such example is WiFi, which allows suitably equipped devices, such as laptop
computers and personal digital assistants, to connect to a wireless access point. The wireless connection is only effective
within a range of approximately 100 meters and at theoretical speeds of up to 54 megabits per second. To address these
limitations, WiFi access points must be placed selectively in high-traffic locations where potential customers frequent
and have sufficient time to use the service. Technology companies are currently developing additional technologies
designed to improve WiFi and otherwise utilize the higher data transmission speeds found in a 3G network. Future
enhancements to the range of WiFi service, such as the emerging WiMax technology, and the networking of WiFi access
points, may provide additional opportunities for mobile wireless operators to deploy hybrid high-mobility 3G and
limited-mobility WiFi networks, each providing capacity and coverage under the appropriate circumstances.
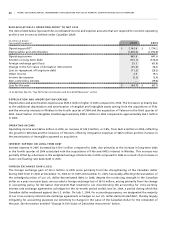
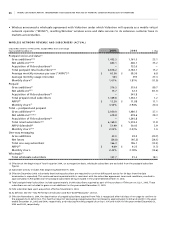
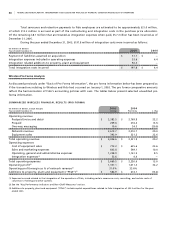
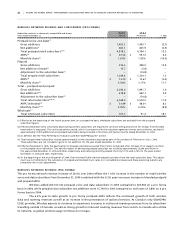
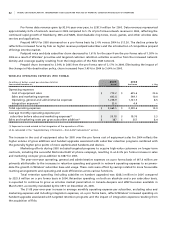
Wireless Operating and Financial Results
For purposes of this discussion, revenue has been classified according to the following categories:
• Network revenue, which includes revenue derived from:
• Postpaid (voice and data), which consists of revenues generated principally from monthly fees, airtime and long-
distance charges, optional service charges, system access fees and roaming charges;
• Prepaid, which consists of revenues generated principally from the advance sale of airtime, usage and long distance
charges; and
• One-way messaging, which consists of revenues generated from monthly fees and usage charges.
• Equipment sales which consists of revenue generated from the sale of hardware and accessories to independent
dealers, agents and retailers, and directly to subscribers through direct fulfillment by Wireless’ customer service
groups, its websites and telesales.