Reebok 2009 Annual Report Download - page 176
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 176 of the 2009 Reebok annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.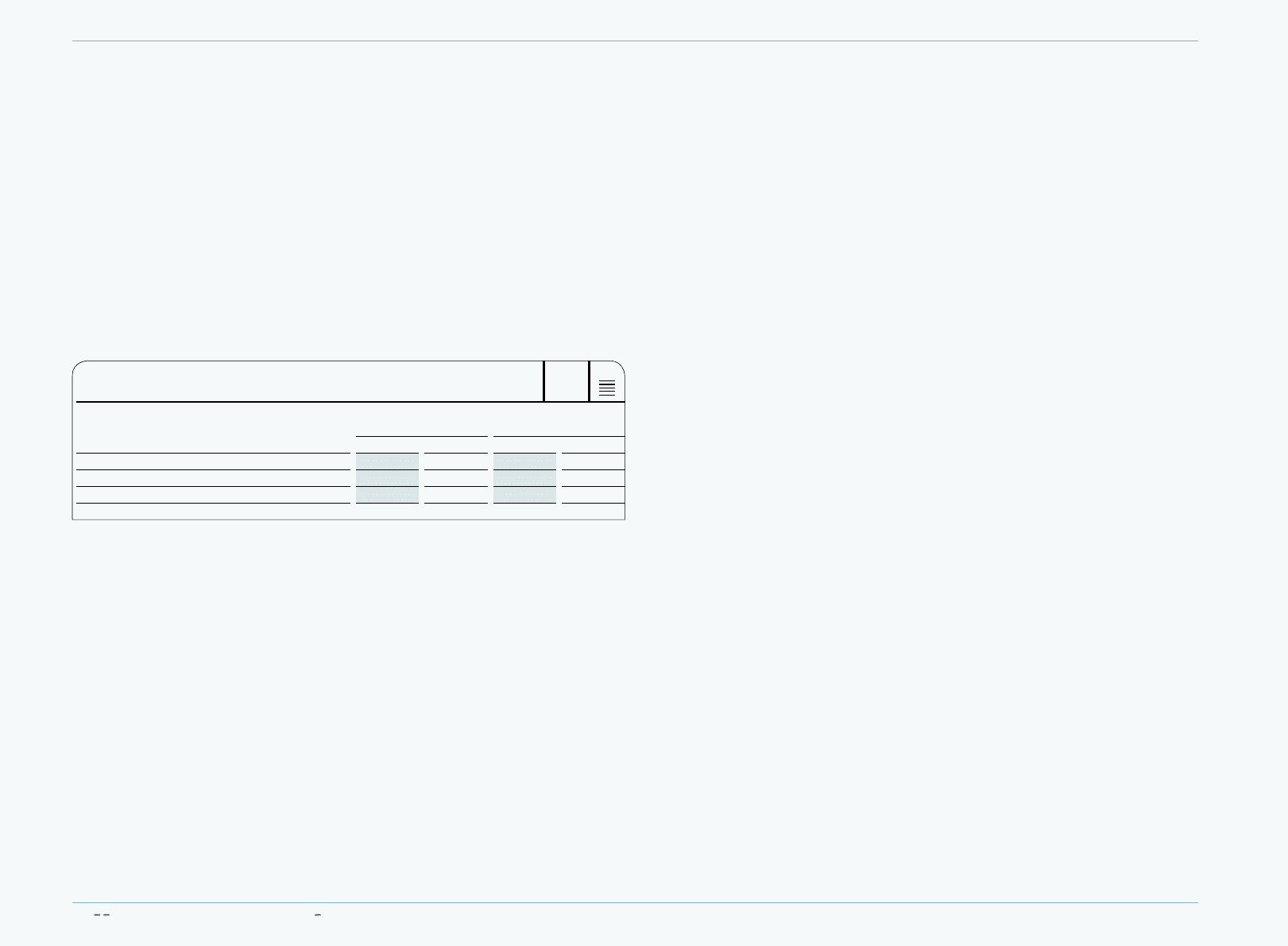
172 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Notes
Currency translation Currency translation
Transactions of assets and liabilities in foreign currencies are translated into the respective func-
tional currency at spot rates on the transaction date.
In the individual financial statements of Group companies, monetary items denominated in
non-functional currencies of the subsidiaries are generally measured at closing exchange rates at
the balance sheet date. The resulting currency gains and losses are recorded directly in income.
Assets and liabilities of the Group’s non-euro functional currency subsidiaries are translated
into the reporting currency, the “euro”, which is also the functional currency of adidas AG, at clos-
ing exchange rates at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at exchange
rates on the transaction dates. All cumulative differences from the translation of equity of foreign
subsidiaries resulting from changes in exchange rates, are included in a separate item within
shareholders’ equity without affecting income.
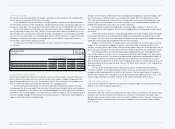
A summary of exchange rates to the euro for major currencies in which the Group operates
is as follows:
N
°-
02
EXCHANGE RATES
€ 1 EQUALS
Average rate for the year
ending Dec. 31 Spot rate
at Dec. 31
2009 2008 2009 2008
USD 1.3932 1.4702 1.4406 1.3917
GBP 0.8912 0.7956 0.8881 0.9525
JPY 130.23 152.39 133.16 126.14
Derivative financial instruments Derivative financial instruments
The Group uses derivative financial instruments, such as currency options, forward contracts as
well as interest rate swaps and cross-currency interest rate swaps, to hedge its exposure to for-
eign exchange and interest rate risks. In accordance with its Treasury Policy, the Group does not
enter into derivative financial instruments with banks for trading purposes.
Derivative financial instruments are initially recognised in the balance sheet at fair value,
and subsequently also measured at their fair value. The method of recognising the resulting gains
or losses is dependent on the nature of the item being hedged. On the date a derivative contract is
entered into, the Group designates certain derivatives as either a hedge of a forecasted transaction
(cash flow hedge), a hedge of the fair value of a recognised asset or liability (fair value hedge) or a
hedge of a net investment in a foreign entity.
Changes in the fair value of derivatives that are designated and qualify as cash flow hedges, and
that are effective, as defined in IAS 39, are recognised in equity. When the effectiveness is not
100%, the ineffective portion of the fair value is recognised in net income. Cumulated gains and
losses in equity are transferred to the income statement in the same periods during which the
hedged forecasted transaction affects the income statement.
For derivative instruments designated as fair value hedges, the gains or losses on the
derivatives and the offsetting gains or losses on the hedged items are recognised immediately in
net income.
Certain derivative transactions, while providing effective economic hedges under the Group’s
risk management policies, may not qualify for hedge accounting under the specific rules of IAS
39. Changes in the fair value of any derivative instruments that do not qualify for hedge accounting
under IAS 39 are recognised immediately in the income statement.
Hedges of net investments in foreign entities are accounted for in a similar way to cash flow
hedges. If, for example, the hedging instrument is a derivative (e.g. a forward contract) or, for
example, a foreign currency borrowing, effective currency gains and losses in the derivative and all
gains and losses arising on the translation of the borrowing, respectively, are recognised in equity.
The Group documents the relationship between hedging instruments and hedged items at
transaction inception, as well as the risk management objectives and strategies for undertaking
various hedge transactions. This process includes linking all derivatives designated as hedges to
specific firm commitments and forecasted transactions. The Group also documents its assess-
ment of whether the derivatives that are used in hedging transactions are highly effective by using
different methods of effectiveness testing, such as the “dollar offset method” or the “hypothetical
derivative method”.
The fair values of forward contracts and currency options are determined on the basis
of market conditions on the reporting dates. The fair value of a currency option is determined
using generally accepted models to calculate option prices. The fair market value of an option is
influenced not only by the remaining term of the option but also by additional factors, such as the
actual foreign exchange rate and the volatility of the underlying foreign currency base.
Cash and cash equivalents Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents represent cash and short-term bank deposits with maturities of three
months or less from the date of acquisition.
Receivables and other assets Receivables and other assets
Receivables and other assets are recognised at fair value, which is estimated as the present value
of future cash flows discounted at the market rate of interest at the balance sheet date. Subse-
quently, these are measured at amortised cost using the “effective interest method”. If necessary,
required allowances are determined on the basis of individual risk assessment and past experi-
ence of losses.