PNC Bank 2006 Annual Report Download - page 110
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 110 of the 2006 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Free-Standing Derivatives
To accommodate customer needs, we also enter into financial
derivative transactions primarily consisting of interest rate
swaps, interest rate caps and floors, futures, swaptions, and
foreign exchange and equity contracts. We primarily manage
our market risk exposure from customer positions through
transactions with third-party dealers. The credit risk associated
with derivatives executed with customers is essentially the
same as that involved in extending loans and is subject to
normal credit policies. We may obtain collateral based on our
assessment of the customer. For derivatives not designated as
an accounting hedge, the gain or loss is recognized in trading
noninterest income.
Also included in free-standing derivatives are transactions that
we enter into for risk management and proprietary purposes
that are not designated as accounting hedges, primarily
interest rate and basis swaps, total return swaps, interest rate
caps and floors, credit default swaps, option contracts and
certain interest rate-locked loan origination commitments as
well as commitments to buy or sell mortgage loans.
Basis swaps are agreements involving the exchange of
payments, based on notional amounts, of two floating rate
financial instruments denominated in the same currency, one
pegged to one reference rate and the other tied to a second
reference rate (e.g., swapping payments tied to one-month
LIBOR for payments tied to three-month LIBOR). We use
these contracts to mitigate the impact on earnings of exposure
to a certain referenced interest rate.
We purchase and sell credit default swaps to mitigate the
economic impact of credit losses on specifically identified
existing lending relationships or to generate revenue from
proprietary trading activities. The fair value of these
derivatives typically is based on the change in value, due to
changing credit spreads.
Interest rate lock commitments for, as well as commitments to
buy or sell, mortgage loans that we intend to sell are
considered free-standing derivatives. Our interest rate
exposure on certain commercial mortgage interest rate lock
commitments is economically hedged with pay-fixed interest
rate swaps and forward sales agreements. These contracts
mitigate the impact on earnings of exposure to a certain
referenced rate.
Free-standing derivatives also include positions we take based
on market expectations or to benefit from price differentials
between financial instruments and the market based on stated
risk management objectives.
Derivative Counterparty Credit Risk
By purchasing and writing derivative contracts we are exposed
to credit risk if the counterparties fail to perform. Our credit
risk is equal to the fair value gain in the derivative contract.
We minimize credit risk through credit approvals, limits,
monitoring procedures and collateral requirements. We
generally enter into transactions with counterparties that carry
high quality credit ratings.
We enter into risk participation agreements to share some of
the credit exposure with other counterparties related to interest
rate derivative contracts or to take on credit exposure to
generate revenue. We will make/receive payments under these
guarantees if a customer defaults on its obligation to perform
under certain credit agreements. Risk participation agreements
entered into prior to July 1, 2003 were considered financial
guarantees and therefore not included in derivatives.
Agreements entered into subsequent to June 30, 2003 are
included in the derivative table that follows. We determine
that we meet our objective of reducing credit risk associated
with certain counterparties to derivative contracts when the
participation agreements share in their proportional credit
losses of those counterparties.
We generally have established agreements with our major
derivative dealer counterparties that provide for exchanges of
marketable securities or cash to collateralize either party’s
positions. At December 31, 2006 we held cash and US
government and mortgage-backed securities with a fair value
of $109 million and pledged cash with a fair value of $151
million under these agreements.
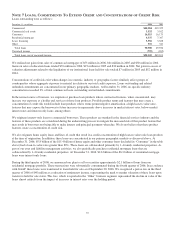
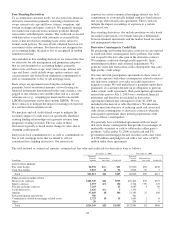
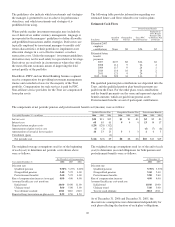
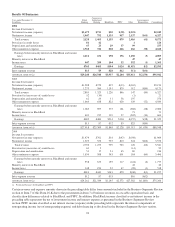
The total notional or contractual amounts, estimated net fair value and credit risk for derivatives were as follows:
December 31, 2006 December 31, 2005
In millions
Notional/
Contract
amount
Estimated net
fair value Credit risk
Notional/
Contract
amount
Estimated net
fair value Credit risk
A
CCOUNTING HEDGES
Fair value hedges $4,996 $(1) $51 $5,900 $78 $108
Cash flow hedges 7,815 62 72 2,926 (9) 5
Total $12,811 $61 $123 $8,826 $69 $113
F
REE
-
STANDING DERIVATIVES
Interest rate contracts $101,749 $21 $533 $70,404 $39 $372
Equity contracts 2,393 (63) 134 2,744 (79) 347
Foreign exchange contracts 7,203 61 4,687 4 60
Credit derivatives 3,626 (11) 5 1,353 7
Options 97,669 68 306 51,383 32 168
Risk participation agreements 786 461
Commitments related to mortgage-related assets 2,723 10 15 1,695 1 6
Other 20 254 5 9
Total $216,169 $25 $1,054 $132,981 $2 $969
100