HSBC 2010 Annual Report Download - page 325
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 325 of the 2010 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327 -
 328
328 -
 329
329 -
 330
330 -
 331
331 -
 332
332 -
 333
333 -
 334
334 -
 335
335 -
 336
336 -
 337
337 -
 338
338 -
 339
339 -
 340
340 -
 341
341 -
 342
342 -
 343
343 -
 344
344 -
 345
345 -
 346
346 -
 347
347 -
 348
348 -
 349
349 -
 350
350 -
 351
351 -
 352
352 -
 353
353 -
 354
354 -
 355
355 -
 356
356 -
 357
357 -
 358
358 -
 359
359 -
 360
360 -
 361
361 -
 362
362 -
 363
363 -
 364
364 -
 365
365 -
 366
366 -
 367
367 -
 368
368 -
 369
369 -
 370
370 -
 371
371 -
 372
372 -
 373
373 -
 374
374 -
 375
375 -
 376
376 -
 377
377 -
 378
378 -
 379
379 -
 380
380 -
 381
381 -
 382
382 -
 383
383 -
 384
384 -
 385
385 -
 386
386 -
 387
387 -
 388
388 -
 389
389 -
 390
390 -
 391
391 -
 392
392 -
 393
393 -
 394
394 -
 395
395 -
 396
396
 |
 |

323
Overview Operating & Financial Review Governance Financial Statements Shareholder Information
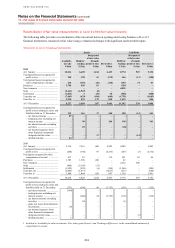
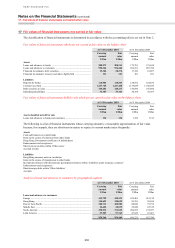
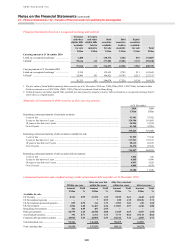
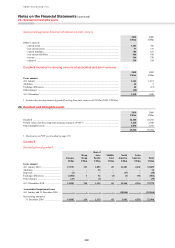
Derivatives are financial instruments that derive their value from the price of underlying items such as equities,
bonds, interest rates, foreign exchange, credit spreads, commodities and equity or other indices. Derivatives enable
users to increase, reduce or alter exposure to credit or market risks. HSBC makes markets in derivatives for its
customers and uses derivatives to manage its exposure to credit and market risks.
Derivatives are carried at fair value and shown in the balance sheet as separate totals of assets and liabilities. A
description of how the fair value of derivatives is derived is set out on page 313. Derivative assets and liabilities on
different transactions are only set off if the transactions are with the same counterparty, a legal right of set-off exists
and the cash flows are intended to be settled on a net basis.
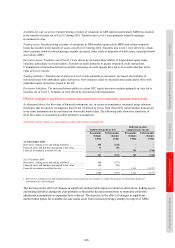
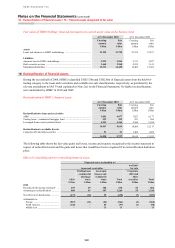
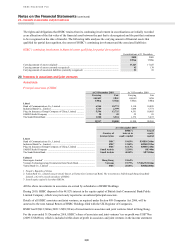
Use of derivatives
HSBC transacts derivatives for three primary purposes: to create risk management solutions for clients, to manage the
portfolio risks arising from client business and to manage and hedge HSBC’s own risks. Derivatives (except for
derivatives which are designated as effective hedging instruments as defined in IAS 39) are held for trading. The held
for trading classification includes two types of derivatives: those used in sales and trading activities, and those used
for risk management purposes but which for various reasons do not meet the qualifying criteria for hedge accounting.
The second category includes derivatives managed in conjunction with financial instruments designated at fair value.
These activities are described more fully below.
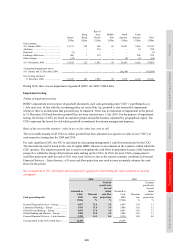
HSBC’s derivative activities give rise to significant open positions in portfolios of derivatives. These positions are
managed constantly to ensure that they remain within acceptable risk levels, with matching deals being utilised to
achieve this where necessary. When entering into derivative transactions, HSBC employs the same credit risk
management procedures to assess and approve potential credit exposures that are used for traditional lending.
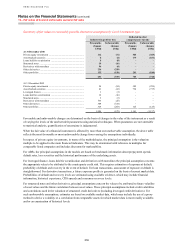
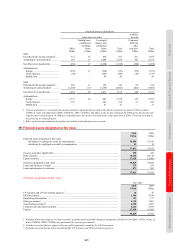
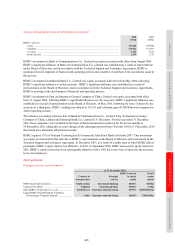
Trading derivatives
Most of HSBC’s derivative transactions relate to sales and trading activities. Sales activities include the structuring
and marketing of derivative products to customers to enable them to take, transfer, modify or reduce current or
expected risks. Trading activities in derivatives are entered into principally for the purpose of generating profits from
short-term fluctuations in price or margin. Positions may be traded actively or be held over a period of time to benefit
from expected changes in exchange rates, interest rates, equity prices or other market parameters. Trading includes
market-making, positioning and arbitrage activities. Market-making entails quoting bid and offer prices to other
market participants for the purpose of generating revenues based on spread and volume; positioning means managing
market risk positions in the expectation of benefiting from favourable movements in prices, rates or indices; arbitrage
involves identifying and profiting from price differentials between markets and products.
As mentioned above, other derivatives classified as held for trading include non-qualifying hedging derivatives,
ineffective hedging derivatives and the components of hedging derivatives that are excluded from assessing hedge
effectiveness. Non-qualifying hedging derivatives are entered into for risk management purposes but do not meet the
criteria for hedge accounting. These include derivatives managed in conjunction with financial instruments
designated at fair value.
Gains and losses from changes in the fair value of derivatives, including the contractual interest, that do not qualify
for hedge accounting are reported in ‘Net trading income’, except for derivatives managed in conjunction with
financial instruments designated at fair value, where gains and losses are reported in ‘Net income from financial
instruments designated at fair value’, together with the gains and losses on the economically hedged items. Where the
derivatives are managed with debt securities in issue, the contractual interest is shown in ‘interest expense’ together
with the interest payable on the issued debt. Substantially all of HSBC Holdings’ derivatives entered into with HSBC
undertakings are managed in conjunction with financial liabilities designated at fair value.
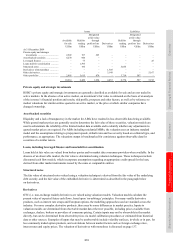
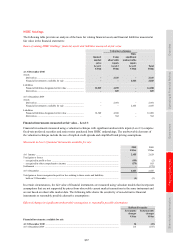
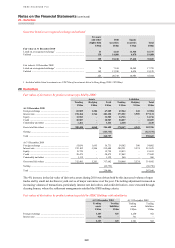
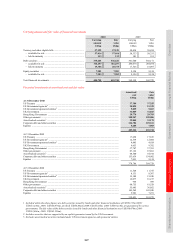
The notional contract amounts of derivatives held for trading purposes indicate the nominal value of transactions
outstanding at the balance sheet date; they do not represent amounts at risk. The 27% increase in the notional
amounts of HSBC’s derivative assets during 2010 was primarily driven by an increase in the number of open
interest rate contracts, reflecting increased trading volumes in the period.
