Reebok 2008 Annual Report Download - page 188
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 188 of the 2008 Reebok annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
184 Consolidated Financial Statements Notes
Due to the short-term maturities of cash and cash equivalents, short-term fi nancial assets,
accounts receivable and payable as well as other current receivables and payables, their respec-
tive fair values approximate their carrying amount.
The fair values of non-current fi nancial assets and liabilities are estimated by discounting
expected future cash fl ows using current interest rates for debt of similar terms and remaining
maturities, and adjusted by an adidas Group specifi c credit risk premium.
Fair values of long-term fi nancial assets classifi ed as available-for-sale are based on quoted
market prices in an active market or are calculated as present values of expected future cash
fl ows.
The fair values of forward contracts and currency options are determined on the basis of market
conditions at the balance sheet date. The fair value of a currency option is determined using
generally accepted models to calculate option prices, such as the “Garman-Kohlhagen-model”.
The fair market value of an option is infl uenced not only by the remaining term of the option, but
also by other determining factors such as the actual foreign exchange rate and the volatility of
the underlying foreign currency base.
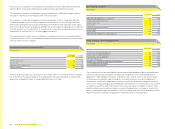
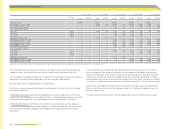
Net gains or (losses) of fi nancial instruments
recognised in the consolidated income statement, € in millions
Year ending
Dec. 31, 2008
Year ending
Dec. 31, 2007
Financial assets or fi nancial liabilities at fair value through profi t or loss (6) (1)
thereof: designated as such upon initial recognition — —
thereof: classifi ed as held for trading (6) (1)
Loans and receivables (27) (18)
Available-for-sale fi nancial assets — —
Financial liabilities measured at amortised cost 11 6
Net gains or losses on fi nancial assets or fi nancial liabilities held for trading include the effects
from fair value measurements of the derivatives that are not part of a hedging relationship,
and changes in the fair value of other fi nancial instruments as well as interest payments which
mainly relate to investment funds.
Net gains or losses on loans and receivables comprise mainly impairment losses and reversals.
Net gains or losses on fi nancial liabilities measured at amortised cost include effects from early
settlement and reversals of accrued liabilities.
The disclosures required by IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures paragraphs 31 – 42
(“Nature and Extent of Risks arising from Financial Instruments”) can be found in the Group
Management Report see Risk and Opportunity Report, p. 107.
Financial instruments for the hedging of foreign exchange risk
The adidas Group uses natural hedges and arranges forward contracts, currency options and
currency swaps to protect against foreign exchange risk. At December 2008, the Group had
contracted currency options with premiums paid totalling an amount of € 5 million (Decem-
ber 31, 2007: € 7 million). The effective part of the currency hedges is directly recognised in
hedging reserves and the acquisition costs of secured inventories, respectively, and posted
into the income statement at the same time as the underlying secured transaction is recorded.
An amount of € 9 million (2007: negative € 10 million) for currency options and an amount
of € 85 million (2007: negative € 51 million) for forward contracts were recorded in hedging
reserves. A total amount of € 6 million impacted net income in 2008 (2007: € 12 million).
The total time value of the currency options not being part of a hedge in an amount of negative
€ 2 million (2007: negative € 9 million) was recorded in the income statement in 2008.
The total net amount of US dollar purchases versus other currencies was US $ 3.6 billion and
US $ 3.0 billion in the years ending December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
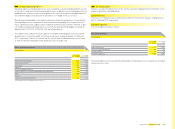
The notional amounts of all outstanding currency hedging instruments, which are mainly related
to cash fl ow hedges, are summarised in the following table:
Notional amounts of all currency hedging instruments
€ in millions
Dec. 31, 2008 Dec. 31, 2007
Forward contracts 2,904 2,317
Currency options 487 562
Total 3,391 2,879
The comparatively high amount of forward contracts is primarily due to currency swaps for
liquidity management purposes and hedging transactions.