SunTrust 2007 Annual Report Download - page 131
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 131 of the 2007 SunTrust annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SUNTRUST BANKS, INC.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
derivatives by establishing and monitoring limits on the types and degree of risk that may be undertaken. The Company
continually measures this risk by using a value-at-risk methodology.
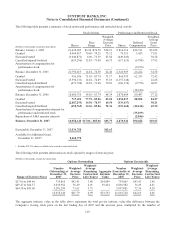
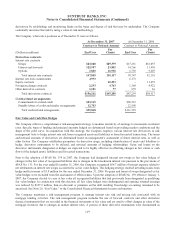
The Company’s derivative positions as of December 31 were as follows:
At December 31, 2007 At December 31, 2006
Contract or Notional Amount Contract or Notional Amount
(Dollars in millions) End User
For
Clients End User
For
Clients
Derivatives contracts
Interest rate contracts
Swaps $23,068 $89,379 $17,231 $61,055
Futures and forwards 122,987 23,802 14,766 11,450
Options 1,800 16,936 6,750 9,605
Total interest rate contracts 147,855 130,117 38,747 82,110
Interest rate lock commitments 4,993 - 6,173 -
Equity contracts - 10,293 - 11,459
Foreign exchange contracts 2,293 4,763 1,360 4,922
Other derivative contracts 1,101 77 979 26
Total derivatives contracts $156,242 $145,250 $47,259 $98,517
Credit-related arrangements
Commitments to extend credit $83,165 $98,512
Standby letters of credit and similar arrangements 12,703 12,998
Total credit-related arrangements $95,868 $111,510
Fair Value and Cash Flow Hedges
The Company utilizes a comprehensive risk management strategy to monitor sensitivity of earnings to movements in interest
rates. Specific types of funding and principal amounts hedged are determined based on prevailing market conditions and the
shape of the yield curve. In conjunction with this strategy, the Company employs various interest rate derivatives as risk
management tools to hedge interest rate risk from recognized assets and liabilities or from forecasted transactions. The terms
and notional amounts of derivatives are determined based on management’s assessment of future interest rates, as well as
other factors. The Company establishes parameters for derivative usage, including identification of assets and liabilities to
hedge, derivative instruments to be utilized, and notional amounts of hedging relationships. Gains and losses on the
derivative instruments designated as hedges are expected to be highly effective in offsetting changes in fair values or cash
flows of the hedged assets, liabilities and forecasted transactions.
Prior to the adoption of SFAS No. 159 in 2007, the Company had designated interest rate swaps as fair value hedges of
changes in the fair value of recognized liabilities due to changes in the benchmark interest rate pursuant to the provisions of
SFAS No. 133. For the year ended December 31, 2006, the Company recognized $64.7 million of interest expense related to
net settlements on interest rate swaps accounted for as fair value hedges. This hedging strategy resulted in trading losses from
hedge ineffectiveness of $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. No gains and losses of swaps designated as fair
value hedges were excluded from the assessment of effectiveness. Upon the adoption of SFAS No. 159 effective January 1,
2007, the Company elected to carry at fair value all recognized liabilities that had previously been designated in qualifying
fair value hedges. In conjunction with this election, all fair value hedges were dedesignated and opening retained earnings
was reduced by $197.2 million, thus no discount or premium on the debt resulting from hedge accounting remained to be
amortized. See Note 20, “Fair Value,” to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information.
The Company maintains a risk management program to manage interest rate risk and pricing risk associated with its
mortgage lending activities. The risk management program includes the use of forward contracts and other derivative
financial instruments that are recorded in the financial statements at fair value and are used to offset changes in value of the
mortgage inventory due to changes in market interest rates. A portion of these derivative instruments were documented as
119