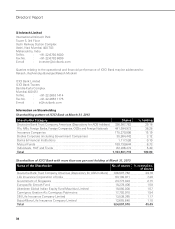
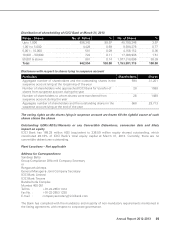
ICICI Bank 2013 Annual Report Download - page 46
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 46 of the 2013 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
44
Business Overview
India continues to remain the largest remittance receiving country in the world and ICICI Bank has a
significant market share in remittances. This has been made possible through our diversified products
and service offerings to meet the requirements of the widely dispersed NRI diaspora. The emphasis
in fiscal 2013 was on further expanding access to remittance services through new partnerships and
channels and delivering a superior customer service experience. ICICI Bank received the Best Remittance
Business Award 2012, at Asia’s prestigious retail banking event, Excellence in Retail Financial Services
Convention, organised by the Asian Banker.
Rural & Inclusive Banking
At the ICICI Group, we view expanding access to banking and other financial services as a critical element
of inclusive growth. During fiscal 2013, we focused on expanding our outreach to rural and semi-urban
markets and providing complete financial solutions to customers in this segment.
We improved our presence in rural markets by expanding our branch and business correspondent network.
During the year, we added 152 rural branches and 85 semi-urban branches, taking the total count of
branches in the rural and semi urban areas to 1,453 at March 31, 2013. This includes 131 low cost Gramin
branches opened in unbanked villages across ten states. These branches provide credit and deposit
products (including 127 Gramin branches opened in fiscal 2013) specifically catering to rural customers.
Our business correspondent network includes over 25 business correspondents with a network of over
7,500 customer service points. We provide micro-savings, remittance and deposit products through this
channel. Technology has been a critical contributor to the success of the business correspondent model,
with the use of innovative technology solutions such as biometric enabled Point of Sale (POS) devices
and mobile handsets. We now cover over 13,500 villages through our branches and business
correspondent network.
At March 31, 2013, we had 14.9 million basic savings bank deposit accounts (also known as no-frills
savings accounts) compared to 9.8 million basic savings bank deposit accounts at March 31, 2012. Apart
from savings products, our rural banking strategy also includes providing a range of asset products like
kisan credit cards, jewel loans, self-help group (SHG) loans, commodity financing to farmers, business
credit for rural enterprises, farm equipment loans and commercial vehicle loans.
We emerged as a leading provider of electronic benefit transfer (EBT) services during fiscal 2013. By
March 31, 2013, we had initiated EBT payment facilities in 48 districts across 11 states. The Bank was
also among the first to implement Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), wherein government social benefits are
directly transferred to the beneficiaries using the Aadhaar platform. DBT payments have been successfully
processed for schemes like Social Security Pension (SSP), Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment
Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), Janani Suraksha Yojna (JSY) and National Rural Health Mission (NRHM)
across four states.
We also made significant progress in scaling up our SHG Bank Linkage Programme. We have differentiated
our offering in this segment by significantly reducing the turnaround time in providing credit. We work
with over 200 entities in this area and have provided credit linkage to about 300,000 individuals, primarily
women, through loans to over 25,000 SHGs, of which over 50% were credit-linked for the first time. Our
progress has been recognised by several agencies including the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural
Development (NABARD).
In urban India, there is a large low-income migrant population which requires customised, low-cost
products that can help them transfer funds to their home towns/villages. To fulfill this need, we have
set up remittance outlets in over 50 major urban centers including Delhi, Mumbai, Surat, Ahmedabad
and Ludhiana. Through these outlets, we have processed over 3,77,000 transactions for over 1,00,000
customers. During the year, we also launched “Mobile Money” in association with telecom companies
like Aircel, Tata Teleservices and Vodafone which targets the urban unbanked population. “Mobile Money”
can be operated through a simple set of instructions using various access channels. It aims at improving
financial inclusion by offering a gamut of financial services such as deposits and cash withdrawals, money
transfer to third parties, recharging of prepaid mobile credit and payment of utility bills.