ICICI Bank 2011 Annual Report Download - page 196
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 196 of the 2011 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F118
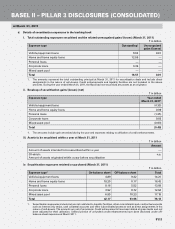
(NII) based on a 100 basis points adverse change in the level of interest rates. The magnitude of the impact over
a one year period, as a percentage of the NII of the previous four quarters gives a fair measure of the earnings
risk that the Bank is exposed to. The EaR computations include the banking book as well as the trading book.
For some of the products, Bank provides its depositors and borrowers an option to terminate the deposit/
loan pre-maturely. These products may or may not provide for a penalty for premature termination. In case of
pre-mature terminations, the Bank faces a risk of re-pricing of the assets/liabilities at the current rates and the
resultant impact on the NII (adjusted for the penalty), over and above the impact as estimated through EAR.
However, the re-pricing/re-investment risk is partly mitigated on account of the premature termination option
in wholesale term deposits and term loans being captured through the behavioral studies implemented in the
interest rate gap statement as mentioned in the earlier paragraphs.
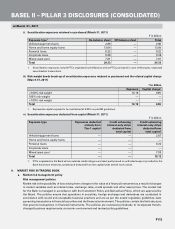
• DoE: Change in the interest rates also have a long-term impact on the market value of equity of the Bank, as
the economic value of the Bank’s assets, liabilities and off-balance sheet positions is impacted . Duration is
a measure of interest rate sensitivity of assets, liabilities and also equity. It may be defined as the percentage
change in the market value of an asset or liability (or equity) for a given change in interest rates. Thus DoE is
a measure of change in the market value of equity of a firm due to the identified change in the interest rates.
The Bank uses DoE as a part of framework to manage IRRBB for its domestic and overseas operations and
the ALM Policy stipulates a limit on the overall DoE of the Bank in order to monitor and manage IRRBB. The
DoE computations include the banking book as well as the trading book. The utilisation against these limits is
computed for appropriate interest rate movements and monitored periodically.
• Stress test for basis risk: The assets and liabilities on the balance sheet are priced based on multiple benchmarks
and when interest rates fluctuate, all these different yield curves may not necessarily move in tandem exposing
the balance sheet to basis risk. Therefore, over and above the EaR, the Bank measures the impact of differential
movement in interest rates across benchmark curves. For the domestic operations various scenarios of interest
rate movements (across various benchmark yield curves) are identified and the worst-case impact is measured
as a percentage of the aggregate of Tier-1 and Tier-2 capital. These scenarios take into account the magnitude
as well as the timing of various interest rate movements (across curves). Currently, the scenarios provide for
differential movements in each yield curve but the movement in each curve is assumed to be parallel. Further,
for the overseas operations of the Bank, assets and liabilities are primarily linked to LIBOR and the basis risk is
computed for a parallel shift in LIBOR as well as spread over LIBOR for the borrowings of the Bank. The basis
risk for the Bank is summations of the risk on domestic and overseas operations.
Most of the other banking entities in the Group, wherever applicable, also monitor IRRBB through similar tools and
limit framework.
Marked-to-market (MTM) on the trading book
In addition to the above, the price risk of the trading book is monitored through a framework of VaR and cumulative
stop loss limits. The trading book includes all fixed income securities in available for sale and held for trading book
including securities held for statutory liquid ratio maintenance purposes in these books, interest rate swaps, and any
other derivatives, which have to be marked to market. The management of price risk of the trading book is detailed in
the Investment Policy.
Hedging policy
Depending on the underlying asset or liability and prevailing market conditions, the Bank enters into hedge
transactions for identified assets or liabilities. The Bank has a policy for undertaking hedge transactions. These
hedges are periodically assessed for hedge effectiveness as per the applicable financial guidelines. The hedges that
meet the effectiveness requirements are accounted for on a basis similar to the underlying asset/liability.
Frameworks in overseas banking subsidiaries
Frameworks that are broadly similar to the above framework have been established at each of the overseas
banking subsidiaries of the Bank to manage interest rate risk in the banking book. The frameworks are established
considering host country regulatory requirements as applicable.
BASEL II – PILLAR 3 DISCLOSURES (CONSOLIDATED)
at March 31, 2011