ICICI Bank 2011 Annual Report Download - page 195
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 195 of the 2011 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F117
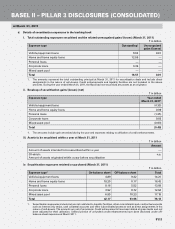
b. Capital requirement for operational risk (March 31, 2011)
As per the RBI guidelines on Basel II, the Bank has adopted Basic Indicator approach for computing capital charge
for operational risk. The capital required for operational risk at March 31, 2011 was ` 26.25 billion.
11. INTEREST RATE RISK IN THE BANKING BOOK (IRRBB)
a. Risk Management Framework for IRRBB
Interest rate risk is the risk of potential variability in earnings and capital value resulting from changes in market
interest rates. IRRBB refers to the risk of deterioration in the positions held on the banking book of an institution
due to movement in interest rates over time. The Bank holds assets, liabilities and off balance sheet items across
various markets with different maturity or re-pricing dates and linked to different benchmark rates, thus creating
exposure to unexpected changes in the level of interest rates in such markets.
Organisational set-up
ALCO is responsible for management of the balance sheet of the Bank with a view to manage the market risk
exposure assumed by the Bank within the risk parameters laid down by the Board of Directors/Risk Committee. A
Global Asset Liability Management (GALM) Group at the Bank monitors and manages the risk under the supervision
of ALCO. Further, the Asset Liability Management (ALM) groups in overseas branches manage the risk at the
respective branches, under direction of the Bank’s GALM group.
The ALM Policy of the Bank contains the prudential limits on liquidity and interest rate risk, as prescribed by
the Board of Directors/Risk Committee/ALCO. Any amendments to the ALM Policy can be proposed by business
group(s), in consultation with the market risk and compliance teams and are subject to approval from ALCO/Risk
Committee/Board of Directors, as per the authority defined in the Policy. The amendments so approved by ALCO
are presented to the Board of Directors/Risk Committee for information/approval.
TMOG is an independent group responsible for preparing the various reports to monitor the adherence to the prudential
limits as per the ALM Policy. These limits are monitored on a regular basis at various levels of periodicity. Breaches,
if any, are duly reported to ALCO/Risk Committee/Board of Directors, as may be required under the framework
defined for approvals/ratification. Upon review of the indicators of IRRBB and the impact thereof, ALCO may suggest
necessary corrective actions in order to realign the exposure with the current assessment of the markets.
Risk measurement and reporting framework
The Bank proactively manages impact of IRRBB as a part of its ALM activities. ALM policy defines the different types
of interest rates risks that are to be monitored, measured and controlled. ALCO decides strategies for managing
IRRBB at the desired level. Further, ALCO periodically gives direction for management of interest rate risk on the
basis of its expectations of future interest rates. Based on the guidance, GALM manages the IRRBB with the help of
various tools i.e. gap analysis, earning at risk (EaR), DoE, stress testing for basis risk etc. These tools are as follows:
• Gap analysis: The interest rate gap or mismatch risk is measured by calculating gaps over different time
intervals at a given date for domestic and overseas operations. Gap analysis measures mismatches between
rate sensitive liabilities (RSL) and rate sensitive assets (RSA) (including off-balance sheet positions). The
report is prepared by grouping rate sensitive liabilities, assets and off-balance sheet positions into time
buckets according to residual maturity or next re-pricing period, whichever is earlier. For non-maturity assets/
liabilities (for instance, working capital facilities on the assets side and current and savings account deposits
on the liabilities side) grouping into time buckets is done based on behavioral studies or by making certain
assumptions. The difference between RSA and RSL for each time bucket signifies the gap in that time bucket.
The direction of the gap indicates whether net interest income is positively or negatively impacted by a change
in the direction of interest rates and the extent of the gap approximates the change in net interest income for
that given interest rate shift. The ALM Policy of the Bank stipulates bucket-wise limits on interest rate gaps for
the domestic operations of the Bank, linked to the networth of the Bank.
• EaR: From an EaR perspective, the gap reports indicate whether the Bank is in a position to benefit from rising
interest rates by having a positive gap (RSA > RSL) or whether it is in a position to benefit from declining
interest rates by a negative gap (RSL > RSA). The Bank monitors the EaR with respect to net interest income
BASEL II – PILLAR 3 DISCLOSURES (CONSOLIDATED)
at March 31, 2011