IBM 2010 Annual Report Download - page 79
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 79 of the 2010 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
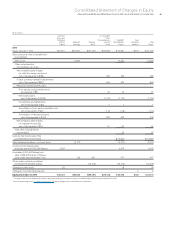
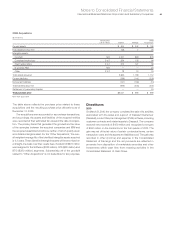
International Business Machines Corporation and Subsidiary Companies 77
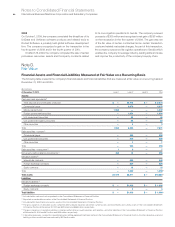
In determining the fair value of financial instruments, the com-
pany considers certain market valuation adjustments to the “base
valuations” calculated using the methodologies described below
for several parameters that market participants would consider in
determining fair value:
•
Counterparty credit risk adjustments are applied to financial
instru ments, taking into account the actual credit risk of a coun-
terparty as observed in the credit default swap market to
determine the true fair value of such an instrument.
• Credit risk adjustments are applied to reflect the company’s
own credit risk when valuing all liabilities measured at fair value.
The methodology is consistent with that applied in developing
counterparty credit risk adjustments, but incorporates the
company’s own credit risk as observed in the credit default
swap market.
As an example, the fair value of derivatives is derived by a discounted
cash flow model using observable market inputs such as known
notional value amounts, yield curves, spot and forward exchange
rates as well as discount rates. These inputs relate to liquid, heavily
traded currencies with active markets which are available for the
full term of the derivative.
Certain financial assets are measured at fair value on a non-
recurring basis. These assets include equity method investments
that are recognized at fair value at the end of the period to the
extent that they are deemed to be other-than-temporarily impaired.
Certain assets that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis
can be subject to nonrecurring fair value measurements. These
assets include public cost method investments that are deemed
to be other-than-temporarily impaired. In the event of an other-
than-temporary impairment of a financial instrument, fair value is
measured using a model described above.
Accounting guidance permits the measurement of eligible
financial assets, financial liabilities and firm commitments at fair
value, on an instrument-by-instrument basis, that are otherwise not
permitted to be accounted for at fair value under other accounting
standards. This election is irrevocable. The company does not
apply the fair value option to any eligible assets or liabilities.
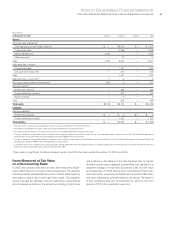
Cash Equivalents
All highly liquid investments with maturities of three months or less
at the date of purchase are considered to be cash equivalents.
Marketable Securities
Debt securities included in current assets represent securities that
are expected to be realized in cash within one year of the balance
sheet date. Long-term debt securities that are not expected to be
realized in cash within one year and alliance equity securities are
included in investments and sundry assets. Debt and marketable
equity securities are considered available for sale and are reported
at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of applicable
taxes, recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss),
a component of equity. The realized gains and losses for available-
for-sale securities are included in other (income) and expense in
the Consolidated Statement of Earnings. Realized gains and losses
are calculated based on the specific identification method.
In determining whether an other-than-temporary decline in
market value has occurred, the company considers the duration
that, and extent to which, the fair value of the investment is below
its cost, the financial condition and near-term prospects of the
issuer or underlying collateral of a security; and the company’s
intent and ability to retain the security in order to allow for an
anticipated recovery in fair value. Other-than-temporary declines
in fair value from amortized cost for available-for-sale equity and
debt securities that the company intends to sell or would more
likely than not be required to sell before the expected recovery of
the amortized cost basis are charged to other (income) and
expense in the period in which the loss occurs. For debt securities
that the company has no intent to sell and believes that it more
likely than not will not be required to sell prior to recovery, only the
credit loss component of the impairment is recognized in other
(income) and expense, while the remaining loss is recognized in
other comprehensive income/(loss). The credit loss component
recognized in other (income) and expense is identified as the
amount of the principal cash flows not expected to be received
over the remaining term of the debt security as projected using
the company’s cash flow projections.
Inventories
Raw materials, work in process and finished goods are stated at
the lower of average cost or market. Cash flows related to the sale
of inventories are reflected in net cash from operating activities in
the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows.
Allowance for Credit Losses
Receivables are recorded concurrent with billing and shipment of
a product and/or delivery of a service to customers. A reasonable
estimate of probable net losses on the value of customer receivables
is recognized by establishing an allowance for credit losses.
Notes and Accounts Receivable—Trade
An allowance for uncollectible trade receivables is estimated based
on a combination of write-off history, aging analysis and any specific,
known troubled accounts.