IBM 2010 Annual Report Download - page 122
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 122 of the 2010 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
International Business Machines Corporation and Subsidiary Companies120
Market liquidity risks are tightly controlled, with only a limited
target percentage of the Qualified PPP portfolio invested in private
market assets consisting of private equities and private real estate
investments, which are less liquid than publicly traded securities.
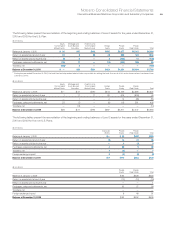
As of December 31, 2010, the Qualified PPP portfolio had $2,909
million in commitments for future investments in private markets
to be made over a number of years. These commitments are
expected to be funded from plan assets.
Derivatives are used on a limited basis as an effective means
to achieve investment objectives and/or as a component of the
plan’s risk management strategy. The primary reasons for the use
of derivatives are fixed income management, including duration,
interest rate management and credit exposure, cash equitization
and as a means to gain exposure to the currency and commodities
markets.
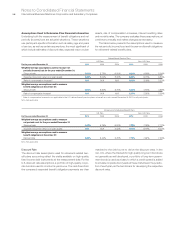
Outside the U.S., the investment objectives are similar to those
described above, subject to local regulations. The weighted-average
target allocation for the non-U.S. plans is 47 percent equity secu-
rities, 46 percent fixed income securities, 2 percent real estate and
5 percent other investments, which is consistent with the allocation
decisions made by the company’s management and is similar to
the prior year weighted-average target allocation. The table on
page 121 details the actual allocations of equity, fixed income, real
estate and all other types of investments for non-U.S. plans. In
some countries, a higher percentage allocation to fixed income
securities is required. In others, the responsibility for managing the
investments typically lies with a board that may include up to 50
percent of members elected by employees and retirees. This can
result in slight differences compared with the strategies previously
described. Generally, these non-U.S. plans do not invest in illiquid
assets and their use of derivatives is usually limited to currency
hedging, adjusting portfolio durations and reducing specific mar-
ket risks. There was no significant change in the investment strat-
egies of these plans during either 2010 or 2009.
The company’s nonpension postretirement benefit plans are
underfunded or unfunded. For some plans, the company maintains
a nominal, highly liquid trust fund balance to ensure timely benefit
payments.
Healthcare Legislation
The expected effects of the U.S. healthcare reform legislation
enacted in March 2010 were incorporated into the remeasurement
of the U.S. nonpension postretirement benefit plan at December 31,
2010. The impact was insignificant as a result of the terms of the
plan which limit the company’ obligation to the participants.
Plan Assets
Retirement-related benefit plan assets are recognized and measured
at fair value as described in note A, “Significant Accounting Policies,”
on page 76. Because of the inherent uncertainty of valuations,
these fair value measurements may not necessarily reflect the
amounts the company could realize in current market transactions.
Investment Policies and Strategies
The investment objectives of the Qualified PPP portfolio are
designed to generate returns that will enable the plan to meet its
future obligations. The precise amount for which these obligations
will be settled depends on future events, including the retirement
dates and life expectancy of the plans’ participants. The obligations
are estimated using actuarial assumptions, based on the current
economic environment and other pertinent factors described on
page 118. The Qualified PPP portfolio’s investment strategy balances
the requirement to generate returns, using potentially higher yielding
assets such as equity securities, with the need to control risk in
the portfolio with less volatile assets, such as fixed-income secu-
rities. Risks include, among others, inflation, volatility in equity
values and changes in interest rates that could cause the plan
to become underfunded, thereby increasing its dependence on
contributions from the company. To mitigate any potential concen-
tration risk, careful consideration is given to balancing the portfo-
lio among industry sectors, companies and geographies, taking
into account interest rate sensitivity, dependence on economic
growth, currency and other factors that affect investment returns.
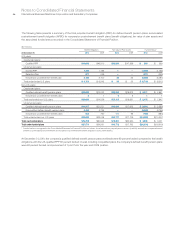
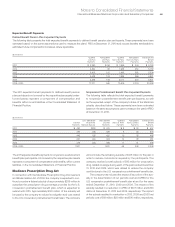
As a result, the Qualified PPP portfolio’s target allocation is 46
percent equity securities, 44 percent fixed income securities, 5 per-
cent real estate and 5 percent other investments, which is consistent
with the allocation decisions made by the company’s management
and is similar to the prior year target allocation. The table on page
121 details the actual allocation of equity, fixed income, real estate
and all other types of investments for the Qualified PPP portfolio.
The assets are managed by professional investment firms and
investment professionals who are employees of the company. They
are bound by investment mandates determined by the company’s
management and are measured against specific benchmarks.
Among these managers, consideration is given, but not limited to,
balancing security concentration, issuer concentration, investment
style and reliance on particular active and passive investment
strategies.