ICICI Bank 2014 Annual Report Download - page 76
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 76 of the 2014 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Management’s Discussion & Analysis
74
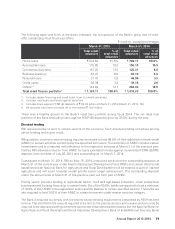
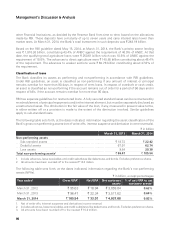
Contingent liabilities decreased from ` 7,899.89 billion at March 31, 2013 to ` 7,814.31 billion at March 31,
2014. The notional principal amount of outstanding forward exchange contracts decreased by 5.2% from
` 2,838.50 billion at March 31, 2013 to ` 2,691.37 billion at March 31, 2014 primarily on account of maturity
of existing deals.
The Bank enters into foreign exchange forwards, options, swaps and other derivative products to enable
customers to transfer, modify or reduce their foreign exchange and interest rate risk and to manage its
own interest rate and foreign exchange positions. The Bank manages its foreign exchange and interest
rate risk with reference to limits set by RBI as well as those set internally. An interest rate swap does not
entail exchange of notional principal and the cash flow arises on account of the difference between interest
rate pay and receive legs of the swaps which is generally much smaller than the notional principal of the
swap. With respect to the transactions entered into with customers, the Bank generally enters into off-
setting transactions in the inter-bank market. This results in generation of a higher number of outstanding
transactions and hence a large value of gross notional principal of the portfolio, while the net market risk is
low. For example, if a transaction entered into with a customer is covered by an exactly opposite transaction
entered into with counter-party, the net market risk of the two transactions will be zero whereas the notional
principal which is reflected as an off-balance sheet item will be the sum of both the transactions.
As a part of project financing and commercial banking activities, the Bank has issued guarantees to support
regular business activities of clients. These generally represent irrevocable assurances that the Bank
will make payments in the event that the customer fails to fulfill its financial or performance obligations.
Financial guarantees are obligations to pay a third party beneficiary where a customer fails to make payment
towards a specified financial obligation. Performance guarantees are obligations to pay a third party
beneficiary where a customer fails to perform a non-financial contractual obligation. The guarantees are
generally for a period not exceeding 10 years. The credit risks associated with these products, as well as the
operating risks, are similar to those relating to other types of financial instruments. Cash margins available
to us to reimburse losses realised under guarantees amounted to ` 52.31 billion at March 31, 2014 and
` 44.29 billion at March 31, 2013. Other property or security may also be available to us to cover losses
under guarantees.
Claims against the Bank, not acknowledged as debts represents demands made in certain tax and legal
matters against the Bank in the normal course of business. In accordance with the Bank’s accounting policy
and Accounting Standard 29, the Bank has reviewed and classified these items as possible obligation based
on legal opinion/judicial precedents/assessment by the Bank. No provision in excess of provisions already
made in the financial statements is considered necessary.
The Bank is obligated under a number of capital contracts. Capital contracts are job orders of a capital
nature, which have been committed. Estimated amounts of contracts remaining to be executed on capital
account in domestic operations aggregated to ` 5.69 billion at March 31, 2014 compared to ` 3.55 billion at
March 31, 2013.
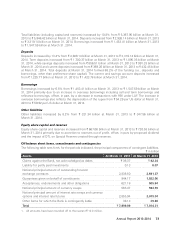
Capital resources
The Bank actively manages its capital to meet regulatory norms and current and future business needs
considering the risks in its businesses, expectations of rating agencies, shareholders and investors and
the available options for raising capital. The capital management framework of the Bank is administered
by the Finance Group and the Risk Management Group under the supervision of the Board and the
Risk Committee. The capital adequacy position and assessment is reported to the Board and the Risk
Committee periodically.
Management’s Discussion & Analysis