ICICI Bank 2014 Annual Report Download - page 64
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 64 of the 2014 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Management’s Discussion & Analysis
62
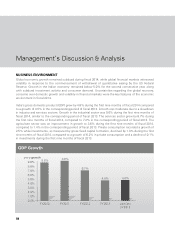
Some important regulatory developments impacting the banking sector during fiscal 2014 were:
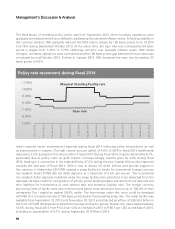
• In May 2013, RBI issued guidelines on restructuring of advances. As per the guidelines, loans that are
restructured (other than due to delay in project completion up to a specified period in the infrastructure
sector and non-infrastructure sector) from April 1, 2015 onwards would be classified as non-performing.
General provision on standard accounts restructured after June 1, 2013 was increased to 5.0%. The
general provision required on standard accounts restructured prior to that date has been increased to
3.5% from March 31, 2014, and would further increase to 4.25% from March 31, 2015 and 5.0% from
March 31, 2016;
• In June 2013, prudential norms pertaining to risk weights, provisioning and loan-to-value ratio for
individual housing loans were revised. Accordingly, individual housing loans of up to ` 7.5 million now
attract risk weight of 50.0% with standard asset provisioning of 0.4%. For individual housing loans of
above ` 7.5 million, the loan-to-value ratio was set at 75.0% and risk weight was lowered from 125.0%
to 75.0%;
• A new category of commercial real estate referred to as commercial real estate - residential housing
was created within the commercial real estate category. Commercial real estate - residential housing
attracts risk weight of 75.0% and standard asset provisioning of 0.75%. Commercial real estate
excluding residential housing has risk weight of 100.0% and standard asset provisioning of 1.0%;
• In August 2013, RBI released a discussion paper on the structure of the banking system in India.
The paper envisages changes in the structure of the banking system with a view to address specific
issues such as enhancing competition, financing higher growth, providing specialised services,
and expanding financial inclusion. The paper proposes to allow different types of banks along with
differentiated licensing for niche services. It also proposes to have continuous licensing for entry of
new banks as against the current system of block licensing. The paper also favors migration from the
current bank-led universal banking model to a financial holding company structure;
• In the first half of fiscal 2014, RBI announced measures with regard to gold imports and financing
of gold during the six months ended September 30, 2013. RBI restricted banks’ import of gold on
consignment basis to only meet the needs of exporters of gold jewellery. Further, import of gold under
all categories was mandated to be only on 100.0% cash margin basis. Advances against the security
of gold coins per customer were restricted to gold coins weighing up to 50 grams;
• In October 2013, RBI liberalised the branch authorisation policy, doing away with the requirement of
approvals to open branches in metropolitan regions. However, the total number of branches opened
in Tier 1 centers during a year cannot exceed the total number of branches opened in Tier 2 to Tier 6
centers during a year. It was also specified that at least 25.0% of total new branches opened in a year
should be in unbanked rural Tier 5 and Tier 6 centers;
• In November 2013, RBI decided to include incremental credit made after November 13, 2013, including
export credit, to medium enterprises as part of priority sector advances. The facility was available up
to March 31, 2014;
• In December 2013, RBI mandated banks to create deferred tax liability, or DTL, on Special Reserve,
with the DTL up to March 31, 2013 permitted to be directly adjusted through reserves and DTL from
the financial year ending March 31, 2014 onwards to be charged through the profit and loss account;
• In December 2013, RBI issued a draft framework on capital surcharges for domestic systemically
important banks (D-SIBs). The higher capital requirements applicable to D-SIBs would be implemented
in a phased manner from April 2016 to April 2019. D-SIBs would be required to have additional Common
Equity Tier 1 capital ranging from 0.2% to 0.8 % of risk weighted assets;
Management’s Discussion & Analysis