IBM 2015 Annual Report Download - page 30
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 30 of the 2015 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.28 Management Discussion
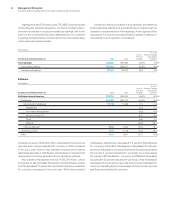
International Business Machines Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
IBM Worldwide Organizations
The following worldwide organizations play key roles in IBM’s deliv-
ery of value to its clients:
• Sales and Distribution
• Research, Development and Intellectual Property
• Integrated Supply Chain
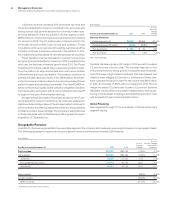
Sales and Distribution
IBM has a significant global presence, operating in more than
175countries, with an increasingly broad-based geographic
distribution of revenue. The company’s Sales and Distribution
organization manages the IBM global footprint, with dedicated
country-based operating units focused on delivering unique value
and a superior client experience. Within these units, client rela-
tionship professionals work with integrated teams of consultants,
product specialists and delivery fulfillment teams to enable clients’
business growth and innovation. These teams deliver value by
understanding the clients’ business and needs, and then bringing
together capabilities from across IBM and an extensive network
of Business Partners to develop and implement client solutions.
By combining global expertise and digital sales capabilities
with local experience, IBM’s geographic structure enables client
relationships through dedicated management focus for local cli-
ents, speed in addressing new market opportunities and timely
investments in emerging opportunities. The geographic units align
industry solution, product and services expertise to serve clients’
agendas. IBM also extends the reach of its capabilities to com-
mercial clients by leveraging industry skills with digital marketing,
digital sales and local Business Partner resources.
The company continues to invest to capture the long-term
opportunity in key growth markets around the world—India, China
and countries within Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe, the Middle
East, Africa and Latin America. The company’s major markets
include the G7 countries of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan,
the United States (U.S.) and the United Kingdom (UK) plus Austria,
the Bahamas, Belgium, the Caribbean region, Cyprus, Denmark,
Finland, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Israel, Malta, the Netherlands,
Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and Switzerland.
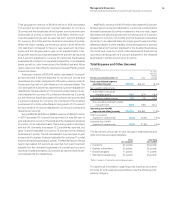
Research, Development and Intellectual Property
IBM’s research and development (R&D) operations differentiate
the company from its competitors. IBM annually invests approxi-
mately 6percent of total revenue for R&D, focusing on high-growth,
high-value opportunities. IBM Research works with clients and
the company’s business units through global labs on near-term
and midterm innovations. It contributes many new technologies
to IBM’s portfolio every year and helps clients address their most
difficult challenges. IBM Research also explores the boundaries
of science and technology—from nanotechnology and future
systems, to big data analytics, secure clouds and advancing the
world’s first cognitive computing platform, IBM Watson.
In 2015, IBM was awarded more U.S. patents than any other
company for the 23rd consecutive year. IBM’s 7,355 patents
awarded in 2015 position the company to compete and lead in
the emerging opportunities represented by big data and analyt-
ics, security, social and mobile technologies. These inventions will
advance IBM’s cloud platform and the new era of computing in
which machines will learn, reason and interact with people in more
natural ways.
The company continues to actively seek intellectual property
(IP) protection for its innovations, while increasing emphasis on
other initiatives designed to leverage its IP leadership. Some of
IBM’s technological breakthroughs are used exclusively in IBM
products, while others are licensed and may be used in IBM prod-
ucts and/or the products of the licensee. While the company’s
various proprietary IP rights are important to its success, IBM
believes its business as a whole is not materially dependent on
any particular patent or license, or any particular group of patents
or licenses. IBM owns or is licensed under a number of patents,
which vary in duration, relating to its products.
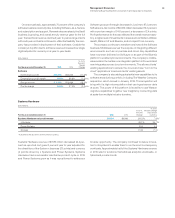
Integrated Supply Chain
IBM has an extensive integrated supply chain, procuring mate-
rials and services globally. In 2015, the company also managed
approximately $24billion in procurement spending for its clients
through the Global Process Services organization. The supply,
manufacturing and logistics operations are seamlessly integrated
and have optimized inventories over time. Simplifying and stream-
lining internal processes has improved sales force productivity and
operational effectiveness and efficiency. Supply chain resiliency
enables IBM to reduce its risk during marketplace changes.
The company continues to derive business value from its own
globally integrated supply chain providing a strategic advantage
for the company to create value for clients. IBM leverages its supply
chain expertise for clients through its supply chain business trans-
formation outsourcing service to optimize and help operate clients’
end-to-end supply chain processes, from procurement to logistics.
Utilizing analytics, mobile, cloud and social—with numerous proj-
ects, has allowed the integrated supply chain to drive positive
business outcomes for the company and its clients.