IBM 2011 Annual Report Download - page 64
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 64 of the 2011 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
62
Management Discussion
International Business Machines Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
variety of financial instruments including derivatives, as explained in
note D, “Financial Instruments,” on pages 96 to 100.
To meet disclosure requirements, the company performs a
sensitivity analysis to determine the effects that market risk exposures
may have on the fair values of the company’s debt and other financial
instruments.
The financial instruments that are included in the sensitivity
analysis comprise all of the company’s cash and cash equivalents,
marketable securities, short-term and long-term loans, commercial
financing and installment payment receivables, investments, long-
term and short-term debt and all derivative financial instruments.
The company’s derivative financial instruments generally include
interest rate swaps, foreign currency swaps and forward contracts.
To perform the sensitivity analysis, the company assesses the
risk of loss in fair values from the effect of hypothetical changes in
interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates on market-
sensitive instruments. The market values for interest and foreign
currency exchange risk are computed based on the present value
of future cash flows as affected by the changes in rates that
are attributable to the market risk being measured. The discount
rates used for the present value computations were selected
based on market interest and foreign currency exchange rates in
effect at December 31, 2011 and 2010. The differences in this
comparison are the hypothetical gains or losses associated with
each type of risk.
Information provided by the sensitivity analysis does not necessarily
represent the actual changes in fair value that the company would
incur under normal market conditions because, due to practical
limitations, all variables other than the specific market risk factor are
held constant. In addition, the results of the model are constrained
by the fact that certain items are specifically excluded from the
analysis, while the financial instruments relating to the financing or
hedging of those items are included by definition. Excluded items
include short-term and long-term receivables from sales-type and
direct financing leases, forecasted foreign currency cash flows and
the company’s net investment in foreign operations. As a consequence,
reported changes in the values of some of the financial instruments
impacting the results of the sensitivity analysis are not matched with
the offsetting changes in the values of the items that those instruments
are designed to finance or hedge.
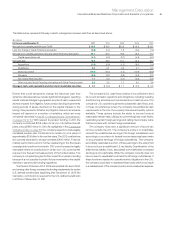
The results of the sensitivity analysis at December 31, 2011, and
2010, are as follows:
Interest Rate Risk
At December 31, 2011, a 10 percent decrease in the levels of interest
rates with all other variables held constant would result in a decrease
in the fair market value of the company’s financial instruments of
$310 million as compared with a decrease of $341 million at
December 31, 2010. A 10 percent increase in the levels of interest
rates with all other variables held constant would result in an increase
in the fair value of the company’s financial instruments of $290 million
as compared to an increase of $315 million at December 31, 2010.
Changes in the relative sensitivity of the fair value of the company’s
financial instrument portfolio for these theoretical changes in the
level of interest rates are primarily driven by changes in the company’s
debt maturities, interest rate profile and amount.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
At December 31, 2011, a 10 percent weaker U.S. dollar against foreign
currencies, with all other variables held constant, would result in an
increase in the fair value of the company’s financial instruments of
$1,303 million as compared with an increase of $546 million at
December 31, 2010. Conversely, a 10 percent stronger U.S. dollar against
foreign currencies, with all other variables held constant, would result
in a decrease in the fair value of the company’s financial instruments
of $1,303 million compared with a decrease of $546 million at
December 31, 2010. The change in impact from 2010 to 2011 was
comprised of: assets ($341 million), debt ($211 million) and derivatives
($205 million).
Financing Risks
See the “Description of Business” on page 24 for a discussion of the
financing risks associated with the Global Financing business and
management’s actions to mitigate such risks.
Cybersecurity
While neither a business segment nor a worldwide organization, the
company’s approach on cybersecurity demonstrates its ability to
adapt to a changing environment, as well as the depth and breadth
of its global capabilities. IBM has leveraged its extensive knowledge
and experience on cybersecurity matters to help its customers. The
company has a suite of software solutions that showcase IBM’s
broad capabilities in identity and access management, data security,
application security, network security and endpoint security. IBM’s
software solutions include a security intelligence dashboard that
can collect information on customer IT security events and provide
detailed information to customers about potential threats and security
posture. The company’s services businesses offer professional
solutions for security from assessment to deployment. In addition,
the company offers managed and outsourced security solutions
from multiple security operations centers around the world. Finally,
security is embedded in a multitude of IBM offerings through secure
engineering processes and by critical functions (encryption, access
control, etc.) in servers, storage, software, services and other solutions.
From an enterprise perspective, IBM has implemented a multi-
faceted approach involving people, tools, and processes to identify
and address cybersecurity risks. The company has established
policies and procedures that provide the foundation by which IBM’s
infrastructure and data are managed, which help protect IBM and
client data. In addition, the company utilizes a combination of online
education, Web articles and other awareness initiatives to enable
its workforce to be knowledgeable about cybersecurity threats and
their responsibilities to identify and mitigate these risks. IBM performs
ongoing assessments regarding its technical controls and its
methods for identifying emerging risks related to cybersecurity. The
company uses a layered approach with overlapping controls to
defend against cybersecurity attacks on networks, end-user devices,
data centers, and applications.