ICICI Bank 2010 Annual Report Download - page 56
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 56 of the 2010 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Management’s Discussion and Analysis
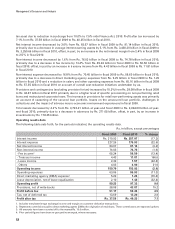
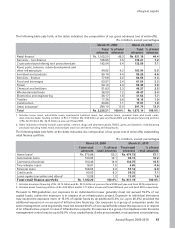
The yield on average interest-earning assets decreased by 116 basis points from 9.1% in fiscal 2009 to 7.9% in
fiscal 2010 primarily due to a decrease in the yield on advances by 111 basis points from 10.2% in fiscal 2009 to
9.1% in fiscal 2010 and a 144 basis points decrease in the yield on earning investments from 7.6% in fiscal 2009
to 6.2% in fiscal 2010. Average balances with RBI decreased from Rs. 189.57 billion in fiscal 2009 to Rs. 120.74
billion in fiscal 2010 primarily due to a reduction in our net demand and time liabilities. During fiscal 2010, CRR was
increased by 75 basis points to 5.75% at year-end fiscal 2010. As CRR balances do not earn any interest income,
the increase in requirement resulted in a negative impact on yield on interest-earning assets.
The overall yield on advances decreased primarily on account of a reduction in the prime lending rate and floating
reference rates for our domestic loan book, a decrease in the benchmark rate (LIBOR) on our overseas loan book
and a decrease in the proportion of high yielding unsecured retail loans in our total loan book. Effective June
5, 2009, we reduced the prime lending rate and the floating reference rate for domestic advances by 100 basis
points each. The decline in the proportion of retail loans in total loans was primarily due to moderation in fresh
retail loan disbursements and contractual repayments and prepayments on the existing portfolio.
During fiscal 2010, interest income was also impacted by lower interest on income tax refund of Rs. 1.21 billion in
fiscal 2010 as compared to Rs. 3.33 billion in fiscal 2009 and loss on securitisation pools (including credit losses
on existing pools) of Rs. 5.09 billion in fiscal 2010 as compared to Rs. 3.21 billion in fiscal 2009. This impact was
reflected over all the quarters of fiscal 2010.
Interest expense decreased by 22.6% from Rs. 227.26 billion in fiscal 2009 to Rs. 175.93 billion in fiscal 2010 due to
a 6.0% decrease in average interest-bearing liabilities from Rs. 3,249.16 billion in fiscal 2009 to Rs. 3,054.87 billion
in fiscal 2010 and a 123 basis points decrease in the cost of funds from 7.0% in fiscal 2009 to 5.8% in fiscal 2010.
Total average interest-bearing liabilities decreased in fiscal 2009 compared to in fiscal 2010 primarily due to a
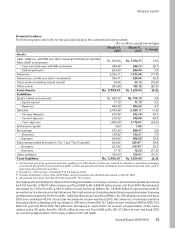
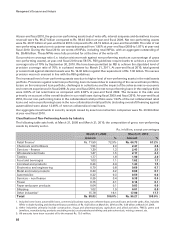
decrease in average deposits. Total deposits decreased by 7.5% from Rs. 2,183.48 billion at year-end fiscal 2009
to Rs. 2,020.17 billion at year-end fiscal 2010. The decrease in total deposits was primarily due to a decrease
in term deposits from Rs. 1,556.80 billion at year-end fiscal 2009 to Rs. 1,178.01 billion at year-end fiscal 2010
due to our conscious strategy of reducing wholesale deposits. During fiscal 2010, our savings account deposits
increased from Rs. 410.36 billion at year-end fiscal 2009 to Rs. 532.18 billion at year-end fiscal 2010, while current
account deposits increased from Rs. 216.32 billion at year-end fiscal 2009 to Rs. 309.98 billion at year-end fiscal
2010. Accordingly, the proportion of current and savings account deposits in total deposits increased from 28.7%
at year-end fiscal 2009 to 41.7% at year-end fiscal 2010. The proportion of average current and savings account
deposits in total average deposits increased from 26.6% in fiscal 2009 to 32.5% in fiscal 2010. Borrowings increased
primarily due to new capital-eligible borrowings in the nature of subordinated debt. Subordinated debt (including
application money towards subordinated debt) increased by 29.4% from Rs. 254.82 billion at year-end fiscal
2009 to Rs. 329.67 billion at year-end fiscal 2010. Borrowings (including subordinated debt) of foreign branches
decreased from USD 10.9 billion at year-end fiscal 2009 to USD 10.8 billion at year-end fiscal 2010. Borrowings
(including subordinated debt) of foreign branches, in rupee terms, decreased from Rs. 551.84 billion at year-end
fiscal 2009 to Rs. 484.46 billion at year- end fiscal 2010.
The decrease in the cost of funds was primarily due to a 140 basis points decrease in the average cost of deposits
from 7.2% in fiscal 2009 to 5.8% in fiscal 2010 and a 88 basis points decrease in the average cost of borrowings
from 6.5% in fiscal 2009 to 5.6% in fiscal 2010. The cost of borrowings decreased due to a decrease in the cost of
foreign currency borrowings and cost of call money borrowings and borrowings under repurchase agreements. The
cost of foreign currency borrowings decreased during fiscal 2010 due to reduction in benchmark rate (LIBOR).
RBI has prescribed a rate of 3.5% on savings deposits and banks were required to pay this interest on the minimum
outstanding balance in a savings account between the 10th day and end of the month. Effective April 1, 2010, RBI has
changed the methodology of computation of the interest payable and banks will be required to pay interest on the
average balance maintained in a savings account. The change in methodology will result in an increased effective
interest rate on savings account deposits and will adversely impact the net interest margin of banks. Our cost of
savings account deposits for the quarter ended March 31, 2010 was 2.9% and in line with the change mentioned
above, would increase to 3.5% from April 1, 2010. Based on average balances for the quarter ended March 31, 2010,
this change is estimated to have an adverse impact of about 10 basis points on our net interest margin.
54