ICICI Bank 2010 Annual Report Download - page 189
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 189 of the 2010 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F109
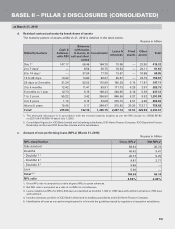
b. Capital requirements for market risk (March 31, 2010)
The capital requirements for market risk (general and specific) at March 31, 2010 were:
Rupees in billion
Risk category Amount
Capital required
- for interest rate risk 25.27
- for foreign exchange (including gold) risk 0.91
- for equity position risk 6.52
10. OPERATIONAL RISK
a. Operational risk management framework
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people or systems, or
from external events. Operational risk includes legal risk but excludes strategic and reputational risk. Operational
risk is inherent in the Bank’s business activities in both domestic as well as overseas operations and, like other
risk types, is managed through an overall framework with checks and balances.
Objectives
The objective of the Bank’s operational risk management is to manage and control operational risks in the
manner specified in the Operational Risk Management Policy (the Policy). The Policy aims at the following:
z Clear ownership and accountability for management and mitigation of operational risk;
z Help business and operations to improve internal controls, reduce likelihood of occurrence of operational
risk incidents and minimise potential impact of losses;
z Minimise losses and customer dissatisfaction due to failure in processes; and
z Develop comprehensive operational risk loss database for effective mitigation.
Operational risk management governance & framework
The Bank’s operational risk management governance and framework risk is defined in the Policy. While the
Policy provides a broad framework, detailed standard operating procedures for operational risk management
processes are established. For the purpose of robust quality of operational risk management across the Bank,
the operational risk management processes of the Bank have been certified for ISO 9001 standard.
The Policy specifies the composition, roles and responsibilities of Operational Risk Management Committee
(ORMC). In line with the RBI guidelines, an independent Operational Risk Management Group (ORMG) was
set up in 2006. The key elements in the operational risk management framework include:
z Identification and assessment of operational risks and controls;
z New products and processes approval framework;
z Measurement through incident and exposure reporting;
z Monitoring through key risk indicators; and
z Mitigation through process and controls enhancement and insurance.
Identification and assessment
Operational risks and controls across the Bank are documented and updated regularly. Each business and
operations group in the Bank has business operational risk managers within the group. ORMG along with these
managers facilitates the business and operation groups for carrying out risk and control self assessments on
a periodic basis as per the plan approved by the ORMC. Risk mitigation plans are monitored to ensure timely
mitigation of risks. Internal controls are tested by Internal Audit Group in the Bank. The testing results are
incorporated in the operational risk assessment. The new product and process approval framework facilitates
detailed review of risks in the products/processes prior to the launch.
Measurement, monitoring, mitigation and reporting
Operational risk incidents are reported regularly and the losses are routed through operational risk account.
Root cause analysis is carried out for the significant operational risk incidents reported and corrective actions
are incorporated back into respective processes.
The Bank has initiated steps to adopt advanced approaches for operational risk capital computation. The Bank is
taking steps to compute capital charge across eight business lines as per the requirements of the standardised
approach for computation of operational risk capital charge. The Bank has been estimating operational value
BASEL II – PILLAR 3 DISCLOSURES (CONSOLIDATED)
at March 31, 2010