ICICI Bank 2010 Annual Report Download - page 183
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 183 of the 2010 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F103
The Bank reckons the permitted credit risk mitigants for obtaining capital relief only when the credit risk mitigant
fulfills the conditions stipulated for eligibility and legal certainty by RBI in its guidelines on Basel II.
Concentrations within credit risk mitigation
The RBI guidelines, among its conditions for eligible credit risk mitigants, require that there should not be a
material positive correlation between the credit quality of the counterparty and the value of the collateral being
considered. CRMG conducts the assessment of the aspect of material positive correlation on cases referred
to it and accordingly evaluates the eligibility of the credit risk mitigant for obtaining capital relief. Currently,
the Bank does not have any concentration risk within credit risk mitigation.
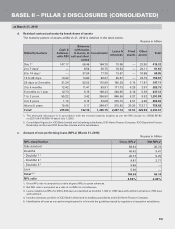
b. Portfolio covered by eligible financial collateral
At March 31, 2010, the credit risk exposures that are covered by eligible financial collateral and guarantees
were as follows:
Rupees in billion
Exposures covered by eligible financial collateral and guarantees Amount1
Exposure before considering eligible financial collateral 178.28
Exposure after considering eligible financial collateral 91.43
Exposures fully covered by eligible guarantees 17.78
1. Includes all entities considered for Basel II capital adequacy computation.
The processes for capital computation and credit risk mitigation based on Basel II guidelines are consistent
across subsidiaries of the Bank.
8. SECURITISATION
a. Securitisation objectives, roles played by the Bank and the risks
Objectives
The Bank’s primary objective of securitisation activities is to increase the efficiency of capital and enhance the
return on capital employed by diversifying sources of funding.
Roles played by the Bank
In securitisation transactions backed by assets either originated by the Bank or third parties, the Bank plays
the following major roles:
z Underwriter: allowing un-subscribed portions of securitised debt issuances, if any to devolve on the
Bank, with the intent of selling at a later stage.
z Investor/trader/market-maker: acquiring investment grade securitised debt instruments backed by
financial assets originated by third parties for purposes of investment/trading/market-making with the
aim of developing an active secondary market in securitised debt.
z Structurer: structuring appropriately in a form and manner suitably tailored to meet investor requirements
while being compliant with extant regulations.
z Provider of liquidity facilities: addressing temporary mismatches on account of the timing differences
between the receipt of cash flows from the underlying performing assets and the fulfillment of obligations
to the beneficiaries.
z Provider of credit enhancement facilities: addressing delinquencies associated with the underlying
assets, i.e. bridging the gaps arising out of credit considerations between cash flows received/collected
from the underlying assets and the fulfillment of repayment obligations to the beneficiaries.
z Provider of collection and processing services: collecting and/or managing receivables from underlying
obligors, contribution from the investors to securitisation transactions, making payments to counterparties/
appropriate beneficiaries, reporting the collection efficiency and other performance parameters and
providing other services relating to collections and payments as may be required for the purpose of
the transactions.
Risks in securitisation
The major risks inherent in the securitised transactions are:
z Credit risk: Risk arising on account of payment delinquencies from underlying obligors/borrowers in the
assigned pool.
BASEL II – PILLAR 3 DISCLOSURES (CONSOLIDATED)
at March 31, 2010