ICICI Bank 2010 Annual Report Download - page 182
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 182 of the 2010 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F102
Collateral management
Overview
The Bank defines collateral as the assets or rights provided to the Bank by the borrower or a third party in
order to secure a credit facility. The Bank would have the rights of secured creditor in respect of the assets/
contracts offered as security for the obligations of the borrower/obligor. The Bank ensures that the underlying
documentation for the collateral provides the bank appropriate rights over the collateral or other forms of credit
enhancement including the right to liquidate, retain or take legal possession of it in a timely manner in the event
of default by the counter party. The Bank also endeavours to keep the assets provided as security to the Bank
under adequate insurance during the tenor of the Bank’s exposure. The collateral is monitored periodically.
Collateral valuation
As stipulated by the RBI guidelines, the Bank uses the comprehensive approach for collateral valuation. Under
this approach, the Bank reduces its credit exposure to a counterparty when calculating its capital requirements
to the extent of risk mitigation provided by the eligible collateral as specified in the Basel II guidelines.
The Bank adjusts the value of any collateral received to adjust for possible future fluctuations in the value of
the collateral in line with the requirements specified by RBI guidelines. These adjustments, also referred to as
‘haircuts’, to produce volatility-adjusted amounts for collateral, are reduced from the exposure to compute
the capital charge based on the applicable risk weights.
Types of collateral taken by the Bank
ICICI Bank determines the appropriate collateral for each facility based on the type of product and risk profile of
the counterparty. In case of corporate and small and medium enterprises financing, fixed assets are generally
taken as security for long tenor loans and current assets for working capital finance. For project finance,
security of the assets of the borrower and assignment of the underlying project contracts is generally taken.
In addition, in some cases, additional security such as pledge of shares, cash collateral, charge on receivables
with an escrow arrangement and guarantees is also taken.
For retail products, the security to be taken is defined in the product policy for the respective products. Housing
loans and automobile loans are secured by the security of the property/automobile being financed. The valuation
of the properties is carried out by an approved valuation agency at the time of sanctioning the loan.
The Bank also offers products which are primarily based on collateral such as shares, specified securities,
warehoused commodities and gold jewellery. These products are offered in line with the approved product
policies which include types of collateral, valuation and margining.
The Bank extends unsecured facilities to clients for certain products such as derivatives, credit cards and personal
loans. The limits with respect to unsecured facilities have been approved by the Board of Directors.
The decision on the type and quantum of collateral for each transaction is taken by the credit approving
authority as per the credit approval authorisation approved by the Board of Directors. For facilities provided
as per approved product policies (retail products, loan against shares etc.), collateral is taken in line with
the policy.
Credit risk mitigation techniques
The RBI guidelines on Basel II allow the following credit risk mitigants to be recognised for regulatory capital
purposes:
z Eligible financial collateral which include cash (deposited with the Bank), gold (including bullion and
jewellery, subject to collateralised jewellery being benchmarked to 99.99% purity), securities issued by
Central and State Governments, Kisan Vikas Patra, National Savings Certificates, life insurance policies
with a declared surrender value issued by an insurance company which is regulated by the insurance
sector regulator, certain debt securities rated by a recognised credit rating agency, mutual fund units
where daily net asset value is available in public domain and the mutual fund is limited to investing in
the instruments listed above.
z On-balance sheet netting, which is confined to loans/advances and deposits, where banks have legally
enforceable netting arrangements, involving specific lien with proof of documentation.
z Guarantees, where these are direct, explicit, irrevocable and unconditional. Further, the eligible guarantors
would comprise:
– Sovereigns, sovereign entities stipulated in the RBI guidelines on Basel II, bank and primary dealers
with a lower risk weight than the counterparty; and
– Other entities, which are rated AA(-) or better.
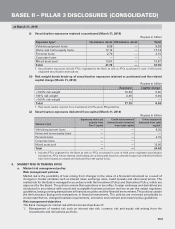
BASEL II – PILLAR 3 DISCLOSURES (CONSOLIDATED)
at March 31, 2010