Nokia 2013 Annual Report Download - page 15
Download and view the complete annual report
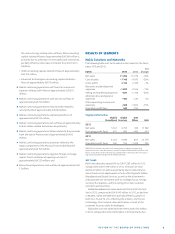
Please find page 15 of the 2013 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.REVIEW BY THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS 13
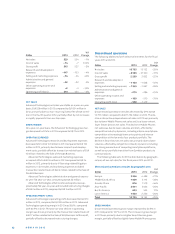
margin. The increase in Smart Devices gross margin was
primarily due to lower inventory related allowances, which
negatively aff ected Smart Devices gross margin in .
OPERATING EXPENSES
Discontinued operations operating expenses were approxi-
mately EUR million in , compared to approximately
EUR million in . The % decrease in was due to
lower Mobile Phones and Smart Devices operating expenses,
primarily due to structural cost savings, as well as overall cost
controls.
OPERATING PROFIT (LOSS)
Discontinued operations operating margin improved to
negative .% in compared to negative .% in . The
improvement was primarily due to structural cost savings, as
well as overall cost controls, and a higher gross margin.
MAIN EVENTS IN 2013
Nokia
■ Nokia completed the acquisition of Siemens’ stake in Nokia
Siemens Networks on August , , making it wholly
owned subsidiary of Nokia. The acquisition was initially
announced on July , . In accordance with this transac-
tion, the Siemens name was phased out from Nokia Siemens
Networks’ company name and branding. The new name and
brand was announced to be Nokia Solutions and Networks,
also referred to as NSN, which was also used for fi nancial
reporting purposes.
■ On September , , Nokia announced that it had signed
an agreement to enter into a transaction whereby Nokia
would sell substantially all of its Devices & Services business
and license its patents to Microsoft.
■ Nokia’s Extraordinary General Meeting held on November ,
confi rmed and approved the Sale of the D&S Business
to Microsoft in line with the proposal and recommendation
of the Nokia Board of Directors. The transaction was com-
pleted on April , .
■ Nokia also announced changes to its leadership as a result
of the announcement of the transaction with Microsoft in
September. To avoid the perception of any potential confl ict
of interest between the announcement and the consum-
mation of the transaction, Stephen Elop stepped aside as
President and CEO of Nokia Corporation, resigned from the
Board of Directors, and became Executive Vice President,
Devices & Services. Risto Siilasmaa assumed an interim CEO
role while continuing to serve in his role as Chairman of the
Nokia Board of Directors and Timo Ihamuotila assumed an
interim President role while also continuing to serve as CFO.
Mr. Ihamuotila also assumed the responsibility of chairing
the Nokia Leadership Team during this interim period. The
interim governance ended on May , after the an-
nouncement of the new strategy and management, includ-
ing the new President and CEO, Rajeev Suri.
■ As a result of the announcement of the Sale of D&S Business,
Nokia Board conducted a strategy evaluation for Nokia
Group, results of which were announced on April , .
Nokia plans to focus on three established businesses:
Networks, a leader in network infrastructure and ser-
vices; HERE, a leader in mapping and location services; and
Technologies, which will build on several of Nokia’s current
CTO and intellectual property rights activities.
Networks operating highlights
■ We won LTE contracts for China Mobile’s and China Telecom’s
nationwide TD-LTE networks; with Chunghwa Telecom in
Taiwan; Celcom in Malaysia; Sprint in the USA; US Cellular’s
second wave of LTE services; with TIM Brasil and Oi Brasil;
Movistar and Claro in Chile; MTS in the Moscow and Central
Russia regions; SFR in Paris; Tele in the Netherland;
Vodafone in New Zealand, and Ooredoo in Qatar.
■ We continued to stay at the forefront of mobile broadband,
further enhancing the Radio Base Station Smart Scheduler
and launching a powerful TD-LTE Base Station radio module;
and introducing new (FlexiZone) microcell and picocell base
stations.
■ Networks and China Mobile enabled the world’s fi rst live TV
broadcast via TD-LTE; NSN and the Singapore-based opera-
tor StarHub completed Southeast Asia’s fi rst GPP standard
Voice over LTE call in a live network. Networks and Panasonic
Mobile Communications were selected by NTT DOCOMO in
Japan to develop for LTE-Advanced next-generation mobile
broadband network architecture; Networks also helped
all three major Korean operators – SK Telecom, LG U+ and
Korea Telecom – to become the world’s fi rst to launch LTE-
Advanced services commercially.
■ Networks and SK Telecom of South Korea completed world’s
fi rst proof-of-concept of Liquid Applications over LTE, and
Networks successfully demonstrated its telco cloud capa-
bilities in a joint proof-of-concept for Evolved Packet Core
(EPC) virtualization with SK Telecom.
■ The Lebanese telecommunications operator, touch, chose
our operations support systems (OSS) portfolio and related
integration services; Zain Kuwait deployed our Customer
Experience Management (CEM) solution, and our CEM con-
tract with Beijing Mobile was extended.