IBM 2008 Annual Report Download - page 77
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 77 of the 2008 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
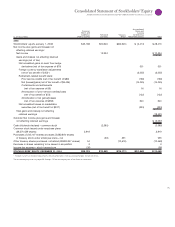
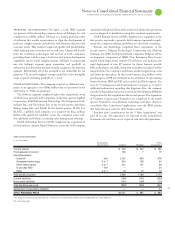
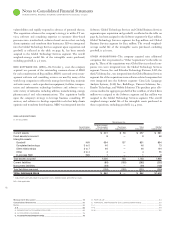
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION and Subsidiary Companies
•
•
Debt securities included in current assets represent securities that are
expected to be realized in cash within one year of the balance sheet
date. Long-term debt securities that are not expected to be realized
in cash within one year and alliance equity securities that are within
the scope of SFAS No. , “Accounting for Certain Investments in
Debt and Equity Securities,” are included in investments and sundry
assets. Those securities are considered available for sale and are
reported at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of appli-
cable taxes, recorded in accumulated gains and
(l
osses) not affecting
retained earnings within stockholders’ equity. Realized gains and
losses are calculated based on the specific identification method.
Other-than-temporary declines in market value from original cost
are charged to other (income) and expense in the period in which the
loss occurs. In determining whether an other-than-temporary decline
in the market value has occurred, the company considers the duration
that, and extent to which, the fair value of the investment is below its
cost. Realized gains and losses also are included in other (income)
and expense in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
Raw materials, work in process and finished goods are stated at the
lower of average cost or market. In accordance with SFAS No. ,
“Statement of Cash Flows,” cash flows related to the sale of inventories
are reflected in net cash from operating activities from continuing
operations in the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows.
Trade
An allowance for uncollectible trade receivables is estimated based on
a combination of write-off history, aging analysis and any specific,
known troubled accounts.
Financing
Financing receivables include sales-type leases, direct financing leases
and loans. The methodologies that the company uses to calculate
both its specific and its unallocated reserves, which are applied con-
sistently to its different portfolios are as follows:
SPECIFIC—The company reviews all financing account receivables
considered at risk on a quarterly basis. The review primarily consists
of an analysis based upon current information available about the
client, such as financial statements, news reports, published credit
ratings, current market-implied credit analysis, as well as the cur-
rent economic environment, collateral net of repossession cost and
prior collection history. For loans that are collateral dependent,
impairment is measured using the fair value of the collateral when
foreclosure is probable. Using this information, the company deter-
mines the expected cash flow for the receivable and calculates a
recommended estimate of the potential loss and the probability of
loss. For those accounts in which the loss is probable, the company
records a specific reserve.
UNALLOCATED—The company records an unallocated reserve that
is calculated by applying a reserve rate to its different portfolios,
excluding accounts that have been specifically reserved. This reserve
rate is based upon credit rating, probability of default, term, asset
characteristics and loss history.
Receivable losses are charged against the allowance when man-
agement believes the uncollectibility of the receivable is confirmed.
Subsequent recoveries, if any, are credited to the allowance.
Certain receivables for which the company recorded specific
reserves may also be placed on non-accrual status. Non-accrual assets
are those receivables (impaired loans or non-performing leases) with
specific reserves and other accounts for which it is likely that the
company will be unable to collect all amounts due according to
original terms of the lease or loan agreement. Income recognition is
discontinued on these receivables. Cash collections are first applied
as a reduction to principal outstanding. Any cash received in excess of
principal payments outstanding is recognized as interest income.
Receivables may be removed from non-accrual status, if appropriate,
based upon changes in client circumstances.
The recorded residual values of the company’s lease assets are esti-
mated at the inception of the lease to be the expected fair value of the
assets at the end of the lease term. The company periodically reassesses
the realizable value of its lease residual values. Any anticipated increases
in specific future residual values are not recognized before realization
through remarketing efforts. Anticipated decreases in specific future
residual values that are considered to be other-than-temporary are
recognized immediately upon identification and are recorded as an
adjustment to the residual-value estimate. For sales-type and direct
financing leases, this reduction lowers the recorded net investment
and is recognized as a loss charged to financing income in the period
in which the estimate is changed, as well as an adjustment to unearned
income to reduce future-period financing income.
Common stock refers to the $. par value per share capital stock as
designated in the company’s Certificate of Incorporation. Treasury
stock is accounted for using the cost method. When treasury stock
is reissued, the value is computed and recorded using a weighted-
average basis.