IBM 2008 Annual Report Download - page 71
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 71 of the 2008 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
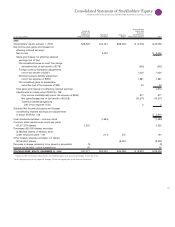
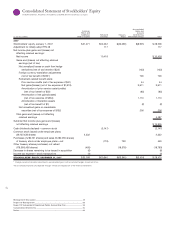
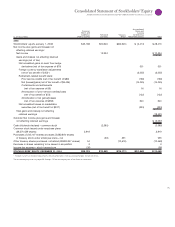
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION and Subsidiary Companies
•
•
Amounts paid to clients in excess of the fair value of acquired assets
used in outsourcing arrangements are deferred and amortized on a
straight-line basis as a reduction of revenue over the expected period
of benefit not to exceed the term of the contract. The company
performs periodic reviews to assess the recoverability of deferred
contract transition and setup costs. This review is done by compar-
ing the estimated minimum remaining undiscounted cash flows of
a contract to the unamortized contract costs. If such minimum
undiscounted cash flows are not sufficient to recover the unamor-
tized costs, a loss is recognized.
Deferred services transition and setup costs were $, million
and $, million at December , and December , ,
respectively. The primary driver of the increase was the
continued
growth of the Global Services business. Amortization expense
of
deferred services transition and setup costs is estimated at December
, to be $ million in , $ million in , $ million
in , $ million in and $ million thereafter.
Deferred amounts paid to clients in excess of the fair value of
acquired assets used in outsourcing arrangements were $ million
and $ million at December , and December , ,
respectively. Amortization of deferred amounts paid to clients in
excess of the fair value of acquired assets is recorded as an offset of
revenue and is estimated at December , to be $ million in
, $ million in , $ million in , $ million in and
$ million thereafter.
In situations in which an outsourcing contract is terminated, the
terms of the contract may require the client to reimburse the com-
pany for the recovery of unbilled accounts receivable, unamortized
deferred costs incurred to purchase specific assets utilized in the
delivery of services and to pay any additional costs incurred by the
company to transition the services.
Costs that are related to the conceptual formulation and design of
licensed programs are expensed as incurred to research, development
and engineering expense; costs that are incurred to produce the fin-
ished product after technological feasibility has been established are
capitalized as an intangible asset. Capitalized amounts are amortized
using the straight-line method, which is applied over periods ranging
up to three years. The company performs periodic reviews to ensure
that unamortized program costs remain recoverable from future
revenue. Costs to support or service licensed programs are charged
to software cost as incurred.
The company capitalizes certain costs that are incurred to pur-
chase or to create and implement internal-use computer software,
which includes software coding, installation, testing and certain data
conversions. These capitalized costs are amortized on a straight-line
basis over two years and are recorded in selling, general and admin-
istrative expense. See note J, “Intangible Assets Including Goodwill,”
on pages and .
The company offers warranties for its hardware products that range
up to three years, with the majority being either one or three years.
Estimated costs for warranty terms standard to the deliverable are
recognized when revenue is recorded for the related deliverable. The
company estimates its warranty costs standard to the deliverable
based on historical warranty claim experience and applies this esti-
mate to the revenue stream for products under warranty. Estimated
future costs for warranties applicable to revenue recognized in the
current period are charged to cost of revenue. The warranty accrual
is reviewed quarterly to verify that it properly reflects the remaining
obligation based on the anticipated expenditures over the balance of
the obligation period. Adjustments are made when actual warranty
claim experience differs from estimates. Costs from fixed-price support
or maintenance contracts, including extended warranty contracts, are
recognized as incurred.
Revenue from extended warranty contracts, for which the company
is obligated to perform, is recorded as deferred income and subse-
quently recognized on a straight-line basis over the delivery period.
Changes in the company’s deferred income for extended warranty
contracts and warranty liability for standard warranties, which are
included in other accrued expenses and liabilities and other liabilities
on the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position, are presented
in the following tables:
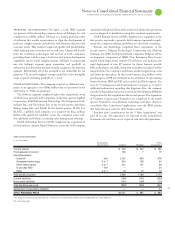
Standard Warranty Liability
($ ) 2008 2007
Balance at January 1 $ 412 $ 582
Current period accruals 390 466
Accrual adjustments to reflect actual experience 16 (29)
Charges incurred (460) (607)
BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31 $ 358 $ 412
Extended Warranty Liability
($ ) 2008 2007
Aggregate deferred revenue at January 1 $ 409 $131
Revenue deferred for new extended
warranty contracts 335 331
Amortization of deferred revenue (134) (61)
Other(a) (21) 7
BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31 $ 589 $409
Current portion $ 234 $161
Noncurrent portion 355 247
BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31 $ 589 $409
(a)
Other consists primarily of foreign currency translation adjustments.