IBM 2008 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2008 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
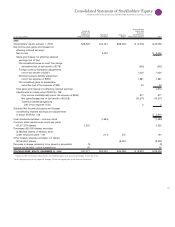
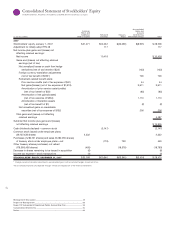
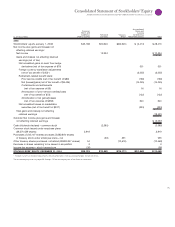
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION and Subsidiary Companies
Management Discussion ............................................................................................. 18
Consolidated Statements ............................................................................................ 60
Notes ............................................................................................................................... 66
A – E ........................................................................................................................66
A. SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES ..........................................................66
B. ACCOUNTING CHANGES .................................................................................76
C. ACQUISITIONS/DIVESTITURES ........................................................................78
D. FAIR VALUE ......................................................................................................84
E. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS (EXCLUDING DERIVATIVES) .................................85
F – J ........................................................................................................................86
K– Q .......................................................................................................................88
R –W ..................................................................................................................... 102
Costs related to shipping and handling are recognized as incurred
and included in cost in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
Selling, General and Administrative
Selling, general and administrative (SG&A) expense is charged to
income as incurred. Expenses of promoting and selling products and
services are classified as selling expense and include such items as
compensation, advertising, sales commissions and travel. General
and administrative expense includes such items as compensation,
office supplies, non-income taxes, insurance and office rental. In
addition, general and administrative expense includes other operat-
ing items such as a provision for doubtful accounts, workforce accru-
als for contractually obligated payments to employees terminated in
the ongoing course of business, amortization of certain intangible
assets and environmental remediation costs.
Advertising and Promotional Expense
The company expenses advertising and promotional costs when
incurred. Cooperative advertising reimbursements from vendors are
recorded net of advertising and promotional expense in the period the
related advertising and promotional expense is incurred. Advertising
and promotional expense, which includes media, agency and promo-
tional expense, was $, million, $, million and $, million
in , and , respectively, and is recorded in SG&A expense
in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
Research, Development and Engineering
Research, development and engineering (RD&E) costs are expensed
as incurred.
Intellectual Property and Custom Development Income
As part of the company’s business model and as a result of ongoing
investment in research and development, the company licenses and
sells the rights to certain of its intellectual property (IP) including
internally developed patents, trade secrets and technological know-
how. Certain transfers of IP to third parties are licensing/royalty-based
and other transfers are transaction-based sales and other transfers.
Licensing/royalty-based fees involve transfers in which the company
earns the income over time, or the amount of income is not fixed or
determinable until the licensee sells future related products (i.e., vari-
able royalty, based upon licensee’s revenue). Sales and other transfers
typically include transfers of IP whereby the company has fulfilled its
obligations and the fee received is fixed or determinable at the transfer
date. The company also enters into cross-licensing arrangements of
patents, and income from these arrangements is recorded only to the
extent cash is received. Furthermore, the company earns income
from certain custom development projects for strategic technology
partners and specific clients. The company records the income from
these projects when the fee is realized or realizable and earned, is not
refundable and is not dependent upon the success of the project.
Other (Income) and Expense
Other (income) and expense includes interest income (other than
from Global Financing external business transactions), gains and
losses on certain derivative instruments, gains and losses from securi-
ties and other investments, gains and losses from certain real estate
transactions, foreign currency transaction gains and losses, gains and
losses from the sale of businesses and amounts related to accretion of
asset retirement obligations.
The company accounts for business combinations using the purchase
method and accordingly, the assets and liabilities of the acquired enti-
ties are recorded at their estimated fair values at the acquisition date.
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair
value of net assets, including the amount assigned to identifiable
intangible assets. The primary drivers that generate goodwill are the
value of synergies between the acquired entities and the company and
the acquired assembled workforce, neither of which qualifies as an
identifiable intangible asset. Identifiable intangible assets with finite
lives are amortized over their useful lives. See note C, “Acquisitions/
Divestitures,” on pages through and note J, “Intangible Assets
Including Goodwill,” on pages and , for additional information.
The results of operations of acquired businesses are included in
the Consolidated Financial Statements from the acquisition date. In
conjunction with the adoption of SFAS No. (R), “Business Com-
bin ations,” the company expensed transaction costs as incurred for
acquisitions not completed in . There are no deferred acquisition
costs recorded on the December , Consolidated Statement of
Financial Position.
Long-lived assets, other than goodwill, are tested for impairment
based on undiscounted cash flows and, if impaired, written down to
fair value based on either discounted cash flows or appraised values.
Goodwill is tested annually for impairment, or sooner when circum-
stances indicate an impairment may exist, using a fair-value approach