IBM 2008 Annual Report Download - page 55
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 55 of the 2008 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Management Discussion
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION and Subsidiary Companies
As a globally integrated enterprise, the company operates in over
countries and is continuing to refocus its business on the higher value
segments of enterprise computing. The company also continues to
rebalance its workforce globally to improve its global reach and com-
petitiveness and to reflect the changing geographic mix of its business.
In , total employees at IBM and its wholly owned subsidiaries
increased , compared with . The U.S. remained the largest
country, with , employees, while resources increased in Asia
Pacific and Latin America and were essentially flat in Europe.
The company continues to add resources aggressively in emerg-
ing markets, particularly in the BRIC countries — Brazil, Russia,
India and China — where employment totals approximately ,.
The complementary workforce is an approximation of equivalent
full-time employees hired under temporary, part-time and limited-
term employment arrangements to meet specific business needs in a
flexible and cost-effective manner.
Global Financing
Global Financing is a reportable segment that is measured as if it
were a standalone entity. Accordingly, the information presented in
this section is consistent with this separate company view.
The mission of Global Financing is to facilitate clients’ acquisi-
tion of IBM hardware, software and services.
Global Financing invests in financing assets, leverages with debt
and manages the associated risks with the objective of generating
consistently strong returns on equity. The primary focus on the com-
pany’s products and clients mitigates many of the risks normally
associated with a financing company. Global Financing has the benefit
of both a deep knowledge of its client base and a clear insight into the
products that are being financed. This combination allows Global
Financing to effectively manage two of the major risks (credit and
residual value) that are normally associated with financing.
Global Financing is comprised of three lines of business:
• Client financing provides lease and loan financing to end users and
internal clients for terms generally between two and seven years.
Internal financing is predominantly in support of Global Services’
long-term client service contracts. Global Financing also factors a
selected portion of the company’s accounts receivable, primarily for
cash management purposes. All internal financing arrangements
are at arm’s-length rates and are based upon market conditions.
• Commercial financing provides primarily short-term inventory
and accounts receivable financing to dealers and remarketers of
IT products.
• Remarketing sells and leases used equipment to new or existing
clients both externally and internally. This equipment is primarily
sourced from the conclusion of lease transactions. Externally-
remarketed equipment revenue represents sales or leases to clients
and resellers. Internally-remarketed equipment revenue primarily
represents used equipment that is sold or leased internally to the
Systems and Technology and Global Services segments. The
Systems and Technology segment may also sell the equipment
that it purchases from Global Financing to external clients.
In addition to the overall health of the economy and its impact on
corporate IT budgets, key drivers of Global Financing’s results are
interest rates and originations. Interest rates directly impact Global
Financing’s business by increasing or decreasing both financing
revenue and the associated borrowing costs. Originations, which
determine the asset base of Global Financing’s annuity-like business,
are impacted by IBM’s non-Global Financing sales volumes and
Global Financing’s participation rates. Participation rates are the
propensity of IBM’s clients to finance their purchases through
Global Financing in lieu of paying IBM up-front cash or financing
through a third party.
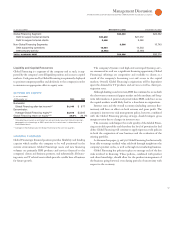
($ )
For the year ended December : 2008 2007 2006
External revenue $2,559 $2,502 $2,365
Internal revenue 1,892 1,482 1,527
Total revenue 4,451 3,984 3,892
Cost 1,887 1,819 1,773
Gross profit $2,564 $2,165 $2,119
Gross profit margin 57.6% 54.4% 54.5%
Pre-tax income $1,617 $1,386 $1,455
After-tax income* $1,049 $ 877 $ 914
Return on equity * 29.4% 26.1% 29.5%
* See page 57 for the details of the after-tax income and return on equity calculation.