Vodafone 2015 Annual Report Download - page 213
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 213 of the 2015 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
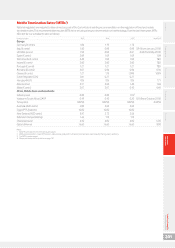
2G 2G networks are operated using global system for mobile (‘GSM’) technology which offers services such as
voice, text messaging and low speed data. In addition, all the Group’s controlled networks support general
packet radio services (‘GPRS’), often referred to as 2.5G. GPRS allows mobile devices to access IP based data
services such as the internet and email.
3G A cellular technology based on wide band CDMA delivering voice and faster data services.
4G/LTE 4G or long-term evolution (‘LTE’) technology offers voice and even faster data transfer speeds than 3G/HSPA.
Acquisition costs The total of connection fees, trade commissions and equipment costs relating to new customer connections.
ADR American depositary receipts is a mechanism designed to facilitate trading in shares of non-US companies
inthe US stock markets. The main purpose is to create an instrument which can easily be settled through
USstock market clearing systems.
ADS American depositary shares are shares evidenced by American depositary receipts. ADSs are issued by a
depositary bank and represent one or more shares of a non-US issuer held by the depositary bank. The main
purpose of ADSs is to facilitate trading in shares of non-US companies in the US markets and, accordingly,
ADRs which evidence ADSs are in a form suitable for holding in US clearing systems.
AGM Annual general meeting.
AMAP The Group’s region: Africa, Middle East and Asia Pacic.
Applications (‘apps’) Apps are software applications usually designed to run on a smartphone or tablet device and provide a
convenient means for the user to perform certain tasks. They cover a wide range of activities including
banking, ticket purchasing, travel arrangements, social networking and games. For example, the
MyVodafoneapp lets customers check their bill totals on their smartphone and see the minutes, texts and
data allowance remaining.
ARPU Average revenue per user, dened as mobile revenue and mobile incoming revenue divided by average
customers.
Capital expenditure (‘capex’) This measure includes the aggregate of capitalised property, plant and equipment additions and capitalised
software costs.
CDMA This is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies.
Churn Total gross customer disconnections in the period divided by the average total customers in the period.
Cloud services This means the customer has little or no equipment at their premises and all the equipment and capability
associated with the service is run from the Vodafone network and data centres instead. This removes the need
for customers to make capital investments and instead they have an operating cost model with a recurring
monthly fee.
Controlled and jointly controlled Controlled and jointly controlled measures include 100% for the Group’s mobile operating subsidiaries and
the Group’s share for joint ventures and the Group’s proportionate share for joint operations.
Customer costs Customer costs include acquisition costs, retention costs and expenses related to ongoing commissions.
Depreciation and other
amortisation
The accounting charge that allocates the cost of a tangible or intangible asset to the income statement
over its useful life. This measure includes the prot or loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment
andcomputer software.
Direct costs Direct costs include interconnect costs and other direct costs of providing services.
EBITDA Operating prot excluding share of results in associates, depreciation and amortisation, gains/losses on the
disposal of xed assets, impairment losses, restructuring costs and other operating income and expense.
TheGroup’s denition of EBITDA may not be comparable with similarly titled measures and disclosures by
other companies.
Enterprise The Group’s customer segment for businesses.
FCA Financial Conduct Authority.
Fixed broadband customer A xed broadband customer is dened as a customer with a connection or access point to a xed line
datanetwork.
FRC Financial Reporting Council.
Free cash ow Operating free cash ow after cash ows in relation to taxation, interest, dividends received from associates
and investments and dividends paid to non-controlling shareholders in subsidiaries but before restructuring
costs and licence and spectrum payments. For the year ended31March 2014 and 31 March 2013, the
income dividends received from Verizon Wireless and payments in respect of a tax case settlement were
alsoexcluded.
HSPA+ An evolution of high speed packet access (‘HSPA’) or third generation (‘3G’) technology that enhances the
existing 3G network with higher speeds for the end user.
IFRS International Financial Reporting Standards.
Impairment A downward revaluation of an asset.
Interconnect costs A charge paid by Vodafone to other xed line or mobile operators when a Vodafone customer calls
acustomer connected to a different network.
IP Internet protocol (‘IP’) is the format in which data is sent from one computer to another on the internet.
IP-VPN A virtual private network (‘VPN’) is a network that uses a shared telecommunications infrastructure, such as
the internet, to provide remote ofces or individual users with secure access to their organisation’s network.
M2M Machine-to-machine. M2M communications, or telemetry, enable devices to communicate with one another
via built-in mobile SIM cards.
Overview Strategy review Performance Governance Financials Additional
information Vodafone Group Plc
Annual Report 2015
211
Denition of terms
Unaudited information