Nokia 2010 Annual Report Download - page 264
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 264 of the 2010 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275
 |
 |
35. Risk Management (Continued)
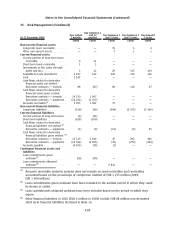
At the end of the years 2010 and 2009, the following currencies represent a significant portion of the
currency mix in the outstanding financial instruments:
2010 USD JPY CNY INR
EURm EURm EURm EURm
FX derivatives used as cashflow hedges (net amount)
(1)
.......... (140) 521 — (23)
FX derivatives used as net investment hedges (net amount)
(2)
..... (642) — (2 834) (702)
FX exposure from balance sheet items (net amount)
(3)
........... (1645) (245) (710) (218)
FX derivatives not designated in a hedge relationship and carried
at fair value through profit and loss (net amount)
(3)
........... 26 645 2129 (95)
Cross currency / interest rate hedges ......................... 408 — — —
2009 USD JPY CNY INR
EURm EURm EURm EURm
FX derivatives used as cashflow hedges (net amount)
(1)
....... (1767) 663 — (78)
FX derivatives used as net investment hedges (net amount)
(2)
. . (969) (6) (983) (208)
FX exposure from balance sheet items (net amount)
(3)
........ (464) (421) (1 358) 80
FX derivatives not designated in a hedge relationship and
carried at fair value through profit and loss (net amount)
(3)
. . (328) 578 1 633 (164)
Cross currency / interest rate hedges ....................... 375 — — —
(1)
The FX derivatives are used to hedge the foreign exchange risk from forecasted highly probable
cashflows related to sales, purchases and business acquisition activities. In some of the
currencies, especially in US Dollar, Nokia has substantial foreign exchange risks in both estimated
cash inflows and outflows, which have been netted in the table. See Note 21 for more details on
hedge accounting. The underlying exposures for which these hedges are entered into are not
presented in the table, as they are not financial instruments as defined under IFRS 7.
(2)
The FX derivatives are used to hedge the Group’s net investment exposure. The underlying
exposures for which these hedges are entered into are not presented in the table, as they are not
financial instruments as defined under IFRS 7.
(3)
The balance sheet items and some probable forecasted cash flows, which are denominated in
foreign currencies, are hedged by a portion of FX derivatives not designated in a hedge
relationship and carried at fair value through profit and loss.
Interest rate risk
The Group is exposed to interest rate risk either through market value fluctuations of balance sheet
items (i.e. price risk) or through changes in interest income or expenses (i.e. refinancing or
reinvestment risk). Interest rate risk mainly arises through interest bearing liabilities and assets.
Estimated future changes in cash flows and balance sheet structure also expose the Group to interest
rate risk.
The objective of Interest rate risk management is to manage uncertainty caused by fluctuations in
interest rates and minimizing net longterm interest rate costs over time.
The interest rate exposure of the Group is monitored and managed centrally. Nokia uses the
ValueatRisk (VaR) methodology to assess and measure the interest rate risk of the net investments
(cash and investments less outstanding debt) and related derivatives.
F76
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
