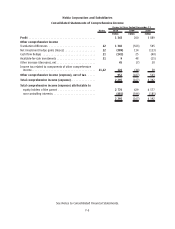
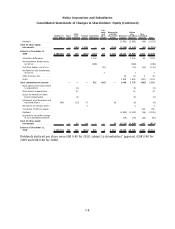
Nokia 2010 Annual Report Download - page 201
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 201 of the 2010 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.1. Accounting principles (Continued)
Pensions
The Group companies have various pension schemes in accordance with the local conditions and
practices in the countries in which they operate. The schemes are generally funded through payments
to insurance companies or to trusteeadministered funds as determined by periodic actuarial
calculations.
In a defined contribution plan, the Group has no legal or constructive obligation to make any
additional contributions if the party receiving the contributions is unable to pay the pension
obligations in question. The Group’s contributions to defined contribution plans, multiemployer and
insured plans are recognized in the income statement in the period to which the contributions relate
for the Group.
All arrangements that do not fulfill these conditions are considered defined benefit plans. If a pension
plan is funded through an insurance contract where the Group does not retain any legal or
constructive obligations, such a plan is treated as a defined contribution plan.
For defined benefit plans, pension costs are assessed using the projected unit credit method: The
pension cost is recognized in the income statement so as to spread the service cost over the service
lives of employees. The pension obligation is measured as the present value of the estimated future
cash outflows using interest rates on high quality corporate bonds with appropriate maturities.
Actuarial gains and losses outside the corridor are recognized over the average remaining service
lives of employees. The corridor is defined as ten percent of the greater of the value of plan assets or
defined benefit obligation at the beginning of the respective year.
Past service costs are recognized immediately in income, unless the changes to the pension plan are
conditional on the employees remaining in service for a specified period of time (the vesting period).
In this case, the past service costs are amortized on a straightline basis over the vesting period.
The liability (or asset) recognized in the statement of financial position is pension obligation at the
closing date less the fair value of plan assets, the share of unrecognized actuarial gains and losses,
and past service costs. Any net pension asset is limited to unrecognized actuarial losses, past service
cost, the present value of available refunds from the plan and expected reductions in future
contributions to the plan.
Actuarial valuations for the Group’s defined benefit pension plans are performed annually. In addition,
actuarial valuations are performed when a curtailment or settlement of a defined benefit plan occurs
in the Group.
Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is
recorded on a straightline basis over the expected useful lives of the assets as follows:
Buildings and constructions ................................. 2033years
Production machinery, measuring and test equipment . ........... 13years
Other machinery and equipment ............................. 310years
Land and water areas are not depreciated.
Maintenance, repairs and renewals are generally charged to expense during the financial period in
which they are incurred. However, major renovations are capitalized and included in the carrying
amount of the asset when it is probable that future economic benefits in excess of the originally
assessed standard of performance of the existing asset will flow to the Group. Major renovations are
F13
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)