Sallie Mae 2015 Annual Report Download - page 8
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 8 of the 2015 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.6
Our Approach to Assisting Students and Families Borrowing and Repaying Private Education Loans
To ensure applicants borrow only what they need to cover their school’s cost of attendance, we actively engage with
schools and require school certification before we disburse a Private Education Loan. To help applicants understand their loan
and its terms, we provide multiple, customized disclosures explaining the applicant’s starting interest rate, the interest rate
during the life of the loan and the loan’s total cost under the available repayment options. Our Smart Option Student Loan
features no origination fees and no prepayment penalties, provides rewards for paying on time, offers a choice of repayment
options, and a choice of either variable or fixed interest rates.
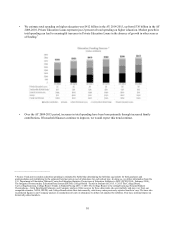
The majority of our Smart Option Student Loan borrowers elect an in-school repayment option. By making in-school
payments, customers learn to establish good repayment patterns, reduce the total loan cost, and graduate with less debt. We
send monthly communications to customers while they are in school, even if they have no monthly payments scheduled, to
keep them informed and encourage them to reduce the amount they will owe when they leave school.
Some customers transitioning from school to the work force may require more time before they are financially capable of
making full payments of principal and interest. Sallie Mae created a Graduated Repayment Program to assist new graduates
with additional payment flexibility, allowing customers to elect to make interest-only payments instead of full principal and
interest payments during the first year after their six-month grace period.
Our experience has taught us the successful transition from school to full principal and interest repayment status involves
making and carrying out a financial plan. As customers approach the principal and interest repayment period on their loans,
Sallie Mae engages with them and communicates what to expect during the transition. In addition, an informational section of
SallieMae.com, Managing Your Loans, provides educational content for borrowers on how to organize loans, set up a monthly
budget, and understand repayment obligations. Examples are provided that help explain how payments are applied and
allocated, and help site visitors estimate payments and see how the accrued interest on alternative repayment programs could
affect the cost of their loans. The site also provides important information on special benefits available to service men and
women under the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act.
After graduation, a customer may apply for the cosigner to be released from the loan. This option is available once there
have been 12 consecutive, on-time principal and interest payments and the student borrower adequately meets our credit
requirements. In the event of a cosigner’s death, the student borrower automatically continues as the sole individual on the loan
with the same terms.
During repayment, customers may struggle to meet their financial obligations. If a customer’s account becomes
delinquent, we will work with the customer and/or the cosigner to understand their ability to make ongoing payments. If the
customer is in financial hardship, we work with the customer and/or cosigner to understand their financial circumstances and
identify any available alternative arrangements designed to reduce monthly payment obligations. These can include extended
repayment schedules, temporary interest rate reductions and, if appropriate, short-term hardship forbearance, suited to their
individual circumstances and ability to make payments.
In some cases, loan modifications and other efforts may be insufficient for those experiencing extreme long term
hardship. Sallie Mae has long supported bankruptcy reform that (i) would permit the discharge of education loans, both private
and federal, after a required period of good faith attempts to repay and (ii) is prospective in application, so as not to rewrite
existing contracts. Any reform should recognize education loans have unique characteristics and benefits as compared to other
consumer loan classes.
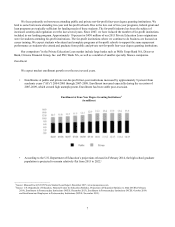
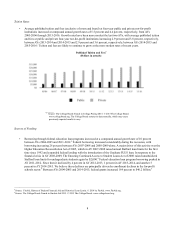
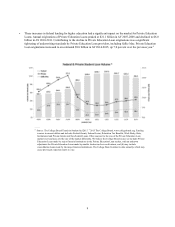
Key Drivers of Private Education Loan Market Growth
The size of the Private Education Loan market is based primarily on three factors: college enrollment levels, the costs of
attending college and the availability of funds from the federal government to pay for a college education. The amounts
students and their families can contribute toward college costs and the availability of scholarships and institutional grants are
also important. If the cost of education increases at a pace exceeding the sum of family income, savings, federal lending, and
scholarships, more students and families can be expected to rely on Private Education Loans. If enrollment levels or college
costs decline or the availability of federal education loans, grants or subsidies and scholarships significantly increases, Private
Education Loan originations could decrease.