ICICI Bank 2012 Annual Report Download - page 193
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 193 of the 2012 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F115
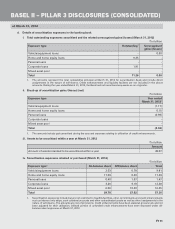
b. Capital requirements for market risk
The capital requirements for market risk (general and specific) at March 31, 2012 were:
` in billion
Amount
Capital required 31.96
- for interest rate risk 1 26.06
- for foreign exchange (including gold) risk 0.87
- for equity position risk 5.03
1. Includes capital required of ` 0.22 billion for securitisation exposure.
10. OPERATIONAL RISK
a. Operational risk management framework
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people or systems, or
from external events. Operational risk includes legal risk but excludes strategic and reputation risk. Operational
risk is inherent in the Bank’s business activities in both domestic as well as overseas operations and covers a wide
spectrum of issues.
Objectives
The objective of the Bank’s operational risk management is to manage and control operational risks in a cost
effective manner within targeted levels of operational risk consistent with the Bank’s risk appetite as specified in
the Operational Risk Management Policy (the Policy) approved by the Board of Directors. The Policy aims to:
Define Bank level operational risk appetite;
Establish clear ownership and accountability for management and mitigation of operational risk;
Help business and operations to improve internal controls, reduce likelihood of occurrence of operational risk
incidents and minimise potential impact of losses;
Minimise losses and customer dissatisfaction due to failure in processes;
Develop comprehensive operational risk loss database for effective mitigation;
Meet regulatory requirements as set out in the guidance note on management of operational risk issued by the
Reserve Bank of India (RBI); and
Compute capital charge for operational risk as per the guidelines issued by the RBI.
Operational risk management governance and framework
The Bank has a comprehensive risk governance structure in line with the RBI guidelines. Further, the Bank is
in compliance with the corporate governance requirements of Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI),
Companies Act and Sarbanes Oxley (SOX) Act (USA). Some of the key sub-committees of the Board that undertake
inter-alia supervision and review of operational risk aspects include the Risk Committee, the Fraud Monitoring
Committee and the Audit Committee.
The Board and the Risk Committee reviews the operational risk level and direction and the material operational risk
exposures. The Fraud Monitoring Committee reviews the fraud risk aspects. The Audit Committee supervises the
audit and compliance related aspects. Internal Audit Department carries out audit according to the Risk Based Audit
Plan and reports the findings to the Audit Committee.
In line with the RBI guidelines, an independent Operational Risk Management Group (ORMG) was set up in the year
2006. The Bank’s operational risk management governance and framework is defined in the Policy. While the Policy
provides a broad framework, detailed standard operating procedures for operational risk management processes
have been established. For the purpose of robust quality of operational risk management across the Bank, the
operational risk management processes of the Bank have been certified for ISO 9001:2008 standard.
The Policy also specifies the composition, roles and responsibilities of Operational Risk Management Committee
(ORMC). ORMC is responsible for overseeing all material operational risks, responses to risk issues and the
adequacy and effectiveness of controls within a given operational risk control area.
BASEL II – PILLAR 3 DISCLOSURES (CONSOLIDATED)
at March 31, 2012