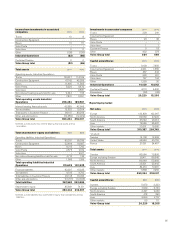
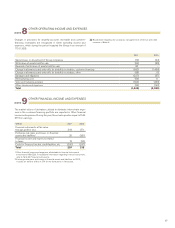
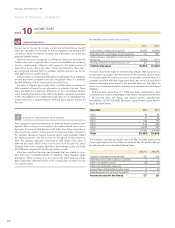
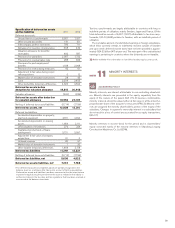
Volvo 2011 Annual Report Download - page 93
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 93 of the 2011 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
CREDIT RISKS
Credit risks are defined as the risk that Volvo does not receive payment for
recognized accounts receivable and customer-financing receivables
(commercial credit risk), that Volvo’s investments are unable to be realized
(financial credit risk) and that potential profit is not realized due to the
counterparty not fulfilling its part of the contract when using derivative
instruments (financial counterparty risk).
POLICY
The objective of the Volvo Group Credit Policy is to define and measure
the credit exposure and control the risk of losses deriving from credits to
customers, credits to suppliers, counter party risks and Customer Dealer
Financing activities.
Commercial credit risk
Volvo’s credit granting is steered by Group-wide policies and customer-
classification rules. The credit portfolio should contain a sound distribu-
tion among different customer categories and industries. The credit risks
are managed through active credit monitoring, follow-up routines and,
where applicable, product repossession. Moreover, regular monitoring
ensures that the necessary allowances are made for incurred losses on
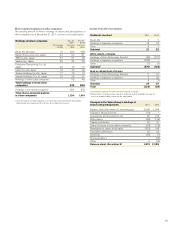
doubtful receivables. In Notes 15 and 16, ageing analyses are presented
of customer finance receivables overdue and accounts receivables over-
due in relation to the reserves made.
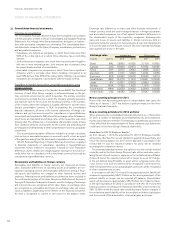
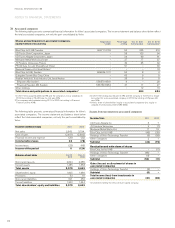
The credit portfolio of Volvo’s customer-financing operations amounted
at December 31, 2011, to approximately net SEK 79 billion (73). The credit
risk of this portfolio is distributed over a large number of retail customers
and dealers. Collaterals are provided in the form of the financed products.
In the credit granting Volvo strives for a balance between risk exposure
and expected return.
Read more about Volvo’s credit risk in the customer-financing operation in
Note 15.
Financial credit risk
The Volvo Group’s financial assets are largely managed by Volvo Treasury
and invested in the money and capital markets. All investments must meet
the requirements of low credit risk and high liquidity. According to Volvo’s
credit policy, counterparties for investments and derivative transactions
should have a rating of A or better from one of the well-established credit
rating institutions.
Financial counterparty risk
The use of derivatives involves a counterparty risk, in that a potential gain
will not be realized if the counterparty fails to fulfill its part of the contract.
To reduce the exposure, master netting agreements are signed, wherever
possible, with the counterparty in question. Counterparty risk exposure for
futures contracts is limited through daily or monthly cash transfers cor-
responding to the value change of open contracts. The estimated gross
exposure to counterparty risk relating to futures, interest-rate swaps and
interest-rate forward contracts, options and commodities contracts
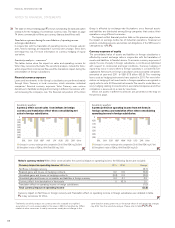
amounted at December 31, 2011, to 281 (331), 4,024 (3,539 ), 284 (190)
and 68 (168).
CREDIT RISKS
89