Volvo 2011 Annual Report Download - page 118
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 118 of the 2011 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
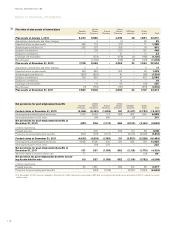
Provision for product warranty
Warranty provisions are estimated with consideration of historical claims
statistics, the warranty period, the average time-lag between faults occurr ing
and claims to the company and anticipated changes in quality indexes.
Estimated costs for product warranties are charged to cost of sales when
the products are sold. Estimated warranty costs include contractual warranty
and goodwill warranty (warranty cover in excess of contractual warranty or
campaigns which is accepted as a matter of policy or normal practice in
order to maintain a good business relation with the customer). Differences
between actual warranty claims and the estimated claims generally affect
the recognized expense and provisions in future periods. Refunds from
suppliers, that decrease Volvo’s warranty costs, are recognized to the
extent these are considered to be certain. At December 31, 2011 warranty
cost provisions amounted to 8,652 (7,841).
Legal proceedings
Volvo recognizes obligations in the Group accounts as provisions or other
liabilities only in cases where Volvo has a present obligation from a past
event, where a financial responsibility is probable and Volvo can make a
reliable estimate of the size of the amount. In instances where these cri-
teria are not met, a contingent liability may be disclosed in the notes to the
accounts.
Volvo regularly reviews the development of significant outstanding
legal disputes in which Group companies are parties, both civil law and tax
disputes, in order to assess the need for provisions and contingent liabili-
ties in the financial statements. Among the factors that Volvo considers in
making decisions on provisions and contingent liabilities are the nature of
the dispute, the amount claimed, the progress of the case, the opinions or
views of legal counsels and other advisers, experience in similar cases,
and any decision of Volvo’s management as to how Volvo intends to han-
dle the dispute. The actual outcome of a legal dispute may deviate from
the expected outcome of the dispute. The difference between actual and
expected outcome of a dispute might materially affect future financial
statements, with an adverse impact upon the Group’s results of operation,
financial position and liquidity.
Read more about the Volvo Group’s gross exposure to contingent liabilities in
Note 24.
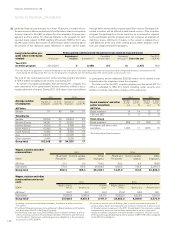
Value in
balance
sheet
2010 Provi-
sions Reversals Utiliza-
tions
Acquired
and
divested
companies
Trans-
lation
differ-
ences
Reclassifica-
tion to assets
held for sale
Other
reclassi-
fica-
tions
Value in
balance
sheet
2011
Of which
due
within 12
months
Of which
due after
12
months
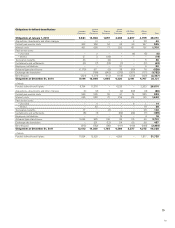
Warranties 7,841 7,718 (1,184) (5,651) (5) 31 (94) (5) 8,652 5,532 3,120
Provisions in insurance
operations 450 186 (49) (101) 0 3 0 0 488 4 484
Restructuring measures 247 123 (17) (152) 0 (1) 0 0 199 166 33
Provisions for residual
value risks 859 167 (63) (226) 1 (5) 0 8 741 290 451
Provisions for service
contracts 444 202 (57) (212) 0 (3) 0 6 380 182 198
Dealer bonus 1,651 3,401 (43) (3,007) 0 3 0 29 2,033 1,892 141
Other provisions 2,978 2,779 (427) (2,471) (18) (60) (65) (32) 2,686 1,467 1,219
Total 14,470 14,576 (1,840) (11,820) (22) (32) (159) 6 15,179 9,533 5,646
Long-term provisions as above is expected to be settled within 2 to 3 years.
SOURCES OF UNCERTAINTY IN ESTIMATES
!
Residual value risks
In the course of its operations, Volvo is exposed to residual value risks
through operating lease agreements and sales combined with repurchase
agreements. Residual value commitments amount to SEK 14,349
(13,339) at December 31, 2011. Residual value risks are reflected in dif-
ferent ways in the Volvo consolidated financial statements depending on
the extent to which the risk remains with Volvo.
In cases where significant risks pertaining to the product remain with
Volvo, the products, primarily trucks, are generally recognized in the bal-
ance sheet as assets under operating leases. Depreciation expenses for
these products are charged on a straight-line basis over the term of the
commitment in amounts required to reduce the value of the product to its
estimated net realizable value at the end of the commitment. The esti-
mated net realizable value of the products at the end of the commitments
is monitored individually on a continuing basis. A decline in prices for used
trucks and construction equipment may negatively affect the consoli-
dated operating income. High inventories in the truck industry and the
construction equipment industry and low demand may have a negative
impact on the prices of new and used trucks and construction equipment.
In monitoring estimated net realizable value of each product under a
residual value commitment, management makes consideration of current
price-level of the used product model, value of options, mileage, condition,
future price deterioration due to expected change of market conditions,
alternative distribution channels, inventory lead-time, repair and recondi-
tioning costs, handling costs and overhead costs in the used product divi-
sions. Additional depreciations and estimated impairment losses are
immediately charged to income.
The total risk exposure for assets under operating lease is reported as
current and non-current residual value liabilities.
Read more in Note 22.
If the residual value risk commitment is not significant, independent from
the sale transaction or in combination with a commitment from the cus-
tomer to buy a new Volvo product in connection to a buy-back option, the
asset is not recognized on balance. Instead, the risk exposure is reported
as a residual value provision equivalent to the estimated residual value
risk.
To the extent the residual value exposure does not meet the definition
of a provision, the remaining residual value risk exposure is reported as a
contingent liability.
Read more in Note 24.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FINANCIAL INFORMATION 2011
114