Nokia 2014 Annual Report Download - page 213
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 213 of the 2014 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
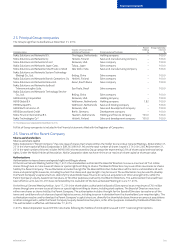
211
Other information
NOKIA IN 2014
Packet: Part of a message transmitted over a packet switched network.
Picocell: A small cellular base station typically covering a small area
typically up to 200 meters wide. Typically used to extend coverage
toindoor areas or to add network capacity in areas with very dense
phone usage, such as train stations.
Platform: Software platform is a term used to refer to an operating
system or programming environment, or a combination of the two.
PND (Portable Navigation Device): A term used to describe portable
devices or devices embedded in a vehicle that are used primarily for
navigation. Smartphones and increasingly feature phones may include
navigation functionalities, but are not generally referred to as PNDs.
Programmable World: Our vision of the future; a world where
connectivity will expand massively, linking people as well as hundreds
of billions of physical objects—from cars, home appliances and
smartphones, to wearables, industrial equipment and health monitors.
What distinguishes the Programmable World from the Internet of
Things is the intelligence that is added to data to allow people to
interpret and use it, rather than just capture it.
RAN (Radio Access Network): A mobile telecommunications system
consisting of radio base stations and transmission equipment.
SDN (Software Dened Networking): An approach to computer
networking that decouples the network control and forwarding
functions enabling the network control to become programmable
and the underlying hardware to be abstracted.
SEPs (Standard-Essential Patents): Generally, patents needed
to produce products which work on a standard, which companies
declare as essential and agree to license on fair, reasonable and
non-discriminatory (FRAND) terms.
Single RAN: Single RAN allows dierent radio technologies to be
provided at the same time from a single base station, using a
multi-purpose platform.
Small cells: low-powered radio access nodes (micro cells or picocell)
and are a vital element to handling very dense data trac demands.
3G and LTE small cells use spectrum licensed by the operator; WiFi
uses unlicensed spectrum which is therefore not under the operator’s
exclusive control.
TD-LTE (Time Division Long Term Evolution, also known as TDD,
Time Division Duplex): An alternative standard for LTE mobile
broadband networks. Time Division means that a single connection
is used alternately to carry data from the base station to the mobile
device (‘downlink’) and then from the mobile device to the base
station (‘uplink’).
TD-SCDMA (Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple
Access): An alternative 3G standard.
Technology licensing: Generally refers to an agreement or
arrangement where under certain terms a company provides another
company with its technology and possibly know-how, whether
protected by intellectual property or not, for use in products or
services oered by the other company.
Telco Cloud: Applying cloud computing, SDN and NFV principles in
telecommunications environment, e.g. separating application software
from underlying hardware with automated, programmable interfaces
while still retaining telecommunications requirements such as high
availability and low latency.
Transmission: The action of conveying signals from one point to one
or more other points.
WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access): A third-generation
mobile wireless technology that oers high data speeds to mobile and
portable wireless devices.
Wi-Fi: A technology enabling an electronic device to transfer data
wirelessly over a network, including high-speed internet connections.
WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access):
A technology of wireless networks that operates according to the
802.16 standard of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers (IEEE).