Nokia 2006 Annual Report Download - page 77
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 77 of the 2006 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Guarantees of Nokia’s performance include EUR 259 million of guarantees that are provided to
certain Networks customers in the form of bank guarantees, standby letters of credit and other
similar instruments. These instruments entitle the customer to claim payment as compensation for
nonperformance by Nokia of its obligations under network infrastructure supply agreements.
Depending on the nature of the instrument, compensation is payable either immediately upon
request, or subject to independent verification of nonperformance by Nokia.
Financial guarantees and securities pledged on behalf of customers represent guarantees relating to
payment by certain third parties under specified credit facilities between such third parties and their
creditors. Nokia’s obligations under such guarantees are released upon the earlier of expiration of
the guarantee or early payment by the customer.
See Note 31 to our consolidated financial statements included in Item 18 of this annual report on
Form 20F for further information regarding commitments and contingencies.
5.C Research and Development, Patents and Licenses
Success in the mobile communications industry requires continuous introduction of new products
and solutions based on the latest available technology. This places considerable demands on our
research and development, or R&D activities. Consequently, in order to maintain our competitiveness,
we have made substantial R&D expenditures in each of the last three years. Our consolidated R&D
expenses for 2006 were EUR 3 897 million, an increase of 2% from EUR 3 825 million in 2005. R&D
expenses in 2004 were EUR 3 776 million. These expenses represented 9.5%, 11.2% and 12.9% of
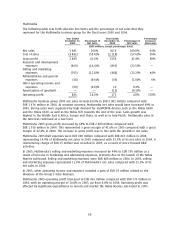
net sales in 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively. In 2006, R&D expenses increased in Multimedia and
Networks and decreased in Mobile Phones and Enterprise Solutions. In 2005, Multimedia incurred a
restructuring charge of EUR 15 million related to R&D activities. R&D expenses in 2004 included
impairments of EUR 115 million in Networks due to the discontinuation of certain products and base
station horizontalization projects and an impairment related to the WCDMA radio access network
project. If the restructuring costs in Multimedia in 2005 (EUR 15 million) and the impairments and
writeoffs of capitalized R&D costs and the restructuring costs in Networks were excluded from 2004
(impairments of EUR 115 million), R&D expenses would have increased 2% in 2006 and 4% in 2005.
This would have represented 9.5% of Nokia net sales in 2006 compared with 11.1% of Nokia net
sales in 2005 and 12.5% of Nokia net sales in 2004.
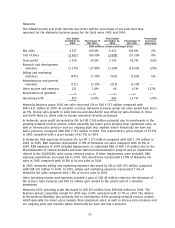
To enable our future growth, we continued to improve the efficiency of our worldwide R&D network
and increased our collaboration with third parties. At December 31, 2006, we employed 21 453
people in R&D, representing approximately 31% of Nokia’s total workforce, and had research and
development presence in 11 countries. R&D expenses of Mobile Phones as a percentage of its net
sales were 5.0% in 2006 compared with 6.0% in 2005 and 6.5% in 2004. In Multimedia, R&D
expenses as a percentage of its net sales were 11.5% in 2006 compared with 14.4% in 2005 and
23.5% in 2004. R&D expenses of Enterprise Solutions as a percentage of its net sales were 30.9%,
compared with 38.2% in 2005 and 36.2% in 2004. In the case of Networks, R&D expenses
represented 15.8%, 17.8% and 18.6% of its net sales in 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively. If the
impairments and writeoffs of capitalized R&D costs and restructuring costs described in the previous
paragraph were excluded, the R&D expenses of Networks would have represented 15.8%, 17.8% and
16.8% of Networks’ net sales in 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively.
We reached our target to lower our mobile device R&D expenses/net sales ratio to 8% by the end of
2006, but we did not reach our target to lower our Networks R&D expenses/net sales ratio to 14%
by the end of 2006. In an effort to continue to improve our efficiency, Nokia targets an improvement
in the ratio of overall Nokia gross margin to R&D expenses in 2007, compared to 2006. See ‘‘Item 4.B
Business Overview—Technology, Research and Development’’ and ‘‘—Patents and Licenses.’’
76