Chrysler 2003 Annual Report Download - page 76
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 76 of the 2003 Chrysler annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
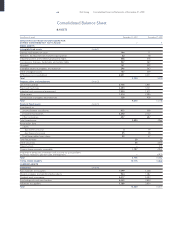
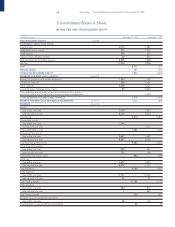
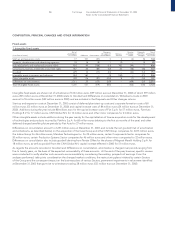
75 Fiat Group Consolidated Financial Statements at December 31, 2003
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Financial receivables are recorded at estimated realizable value.
Securities are recorded at cost, including additional direct
charges. In the event of permanent impairment, a valuation
allowance is provided as a direct reduction of the securities.
However, in the balance sheet at December 31, 2002, securities
held by the insurance companies as investments for the benefit
of those insured under life insurance policies, where the insured
parties bear the risk (relating to index-linked and unit-linked
policies), and as investments in the management of pension
funds, were presented under a separate caption and valued
at market price, as set forth by the specific regulations of the
insurance industry in Italy.
Treasury stock held as fixed assets is recorded at purchase
cost, including any writedowns resulting from a permanent
impairment in its value. A specific reserve for treasury stock
is also recorded under stockholders’ equity of the Group for
the same amount.
Financial fixed assets include finance lease contracts receivables,
recorded at cost. The related depreciation is calculated,
according to the financial method, based on the life of the
lease and the related risk in managing such contracts.
Current assets
Inventories of raw materials, semifinished products, finished
goods and contract work in progress completed within the
fiscal year are valued at the lower of cost or market, cost being
determined on a First In-First-Out (FIFO) basis. The valuation
of inventories includes the direct costs of materials, labor and
variable and fixed indirect costs. Provision is made for obsolete
and slow-moving raw materials, finished goods, spare parts
and other supplies based on their expected future use and
realizable value.
Work in progress on long-term contracts is valued based on
the stage of completion and is recorded gross of advance
payments received from customers. Eventual losses on such
contracts are fully recorded when they become known.
Receivables are recorded at estimated realizable value. Any
unearned interest included in the nominal value of financial
receivables has been deferred to future periods. Receivables
sold to third parties with recourse or without recourse (including
those sold as part of securitization transactions) are eliminated
from receivables and disclosed in the memorandum accounts.
Receivables denominated in foreign currency are translated at
the exchange rate in effect at year end. Resulting exchange
gains and losses are included in the statement of operations.
Other receivables also include deposits to guarantee the
securitization transactions of trade receivables (securitization
refers to particular programs of discounting trade receivables
without recourse, with a collateral deposit as a guarantee).
Current assets also include investments and securities acquired
as short-term investments which are valued at the lower of cost
or market, cost being determined on a Last-In First-Out (LIFO)
basis.
Treasury stock consists of Fiat S.p.A. shares bought back by
Fiat Ge.Va. S.p.A. and by Fiat; it is valued at the lower of cost
or market, cost being determined on a Last-In First-Out (LIFO)
basis. A specific reserve for treasury stock is also recorded under
the stockholders’ equity of the Group for the same amount.
Reserves for risks and charges and employee severance
indemnities
The reserves for risks and charges include provisions to cover
losses or liabilities likely to be incurred but uncertain as to the
amount or as to the date on which they will arise.
In particular, the reserve for pensions and similar obligations
includes provisions for long-service or other bonuses (including
pension funds required by some countries in which the Group
operates), payable to employees and former employees under
contractual agreements or by law, determined on an actuarial
basis, where applicable.
Restructuring reserves include the costs to carry out corporate
reorganization and restructuring plans and are provided in the
year the company formally decides to commence such plans
and the relative costs can be reasonably estimated.
The policy liabilities and accruals of insurance companies are
determined according to the procedures and rules issued by
the regulatory agencies in each country in which the individual
subsidiaries operate. In particular, unearned property and
liability premiums are recognized on the pro-rata basis over
the period of the policy. The reserve for unpaid property and
liability losses and unpaid adjustment expenses has been
calculated on the basis of reasonable estimates of the “latest
cost” of the claims, analytically and for groups of particular risks,
following adequate statistical and actuarial methods. The policy
liabilities and accruals for unpaid losses on life insurance claims
are calculated on an actuarial basis, accompanied by an opinion
by a qualified actuary on the congruity of the amount. Finally,
as previously described, the policy liabilities and accruals
against investments made for the benefit of those insured
under life insurance policies, where the insured parties bear the
risk (related to index-linked and unit-linked policies), and those
deriving from the management of pension funds are presented
under a separate caption, as set forth by the specific regulations
of the insurance industry in Italy.
The reserve for employee severance indemnities comprises
liability for severance indemnities that Italian companies accrue
each year end for employees, as determined in accordance with
labor legislation. In particular, the liability includes a portion of
the employee’s annual salary and is indexed for inflation in
accordance with Italian rules.
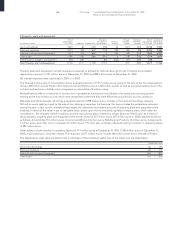
Payables
Payables are recorded at face value; the portion of interest
included in the nominal amount is deferred until future periods
in which it is earned. Accounts payable denominated in foreign