Volvo 2006 Annual Report Download - page 136
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 136 of the 2006 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
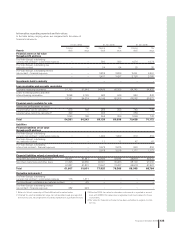
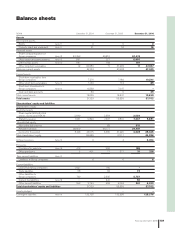
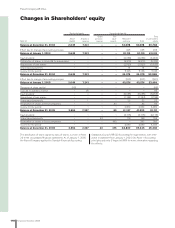
132 Financial information 2006
The Volvo Group
Notes to consolidated financial statements
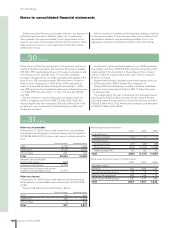
The following table shows the reported values of the fi nancial
assets as they mature. In all cases, these assets are exposed to an
interest-rate risk.
Assets with Assets with Total fi nancial
SEK M fi xed interest variable interest assets
2007 13,804 25,655 39,459
2008–2009 75 1,523 1,598
2010 and later 32 – 32
13,911 27,178 41,089
Excluding net receivable for pensions, SEK 2.032 M and interest-
bearing assets held for sale, SEK 5 M.
Currency risks
The content of the reported balance sheet may be affected by
changes in different exchange rates. Currency risks in Volvo’s oper-
ations are related to changes in the value of contracted and expected
future payment fl ows (commercial currency exposure), changes in
the value of loans and investments (fi nancial currency exposure) and
changes in the value of assets and liabilities in foreign subsidiaries
(currency exposure of shareholders’ equity). The aim of Volvo’s cur-
rency-risk management is to minimize, over the short term, negative
effects on Volvo’s earnings and fi n ancial position stemming from
exchange-rate changes.
Commercial currency exposure
In order to hedge the value of future payment fl o ws in foreign cur-
rencies, Volvo uses forward contracts and currency options. Accord-
ing to the Group’s currency policy, for each currency, 50–80% of the
forecast net fl o w in the next six months is hedged and 30–60% for
months seven to 12, while contracted fl o ws after 12 months should
normally not be hedged. A decision concerning changes in the
Group’s currency policy has been made, effective 2007. For each
currency, 75% of the forecast net fl o ws for the coming six months
are to be hedged and 50% for months seven to 12, while contracted
fl o w s after 12 months should normally be hedged. The nominal
amount of all outstanding forward and option contracts amounted to
SEK 57.2 billion at December 31, 2006. On the same date, the fair
value of these contracts was positive in an amount of 764 (negative
732).
Assuming that at a certain time the Swedish krona appreciated by
10% against all foreign currencies, the fair value of outstanding con-
tracts would amount to 3,252. If, instead, at a certain time the Swed-
ish krona was devalued by 10%, the fair value of outstanding con-
tracts would be negative in an amount of 1,724. In reality, currencies
usually do not change in the same direction at any given time, so the
actual effect of exchange-rate changes may differ from the above
sensitivity analysis.
Financial currency exposure
Loans and investments in the Group’s subsidiaries are done mainly
through Volvo Treasury in local currencies, which minimizes individ-
ual companies’ fi nancial currency exposure. Volvo Treasury uses vari-
ous derivatives, in order to facilitate lending and borrowing in differ-
ent currencies without increase the company’s own risk. The fi n ancial
net position of the Volvo Group is affected by exchange rate fl u ctua-
tions, since fi n ancial assets and liabilities are distributed among
Group companies that conduct their operations in different currencies.
Currency exposure of shareholders’ equity
The consolidated value of assets and liabilities in foreign subsidiar-
ies is affected by current exchange rates in conjunction with transla-
tion of assets and liabilities to Swedish kronor. To minimize currency
exposure of shareholders’ capital, the size of shareholders’ equity in
foreign subsidiaries is continuously optimized with respect to com-
mercial and legal conditions. Currency hedging of shareholders’
equity may occur in cases where a foreign subsidiary is considered
overcapitalized. Net assets in foreign subsidiaries and associated
companies amounted at year-end 2006 to SEK 43.6 bn (33.7). Of
this amount, SEK 3.6 bn (0.8) was currency-hedged through loans in
foreign currencies. Out of the loans used as hedging instruments
SEK 2.8 billion are due in 2010 and the remaining SEK 0.8 bllion in
the need to undertake currency hedging relating to investments in
associated companies and other companies is assessed on a case-
by-case basis.
Credit risks
Volvo’s credit provision is steered by Group-wide policies and cus-
tomer-classifi cation rules. The credit portfolio should contain a
sound distribution among different customer categories and indus-
tries. The credit risks are managed through active credit monitoring,
follow-up routines and, where applicable, product reclamation. More-
over, regular monitoring ensures that the necessary provisions are
made for uncertain receivables.
The credit portfolio of Volvo’s customer-fi nancing operations
amounted at December 31, 2006, to approximately SEK 77 bn. The
credit risk of this portfolio is distributed over a large number of retail
customers and dealers. Collateral provided in the form of the
fi n a nced products. Credit provision aims for a balance between risk
exposure and expected yield. The Volvo Group’s fi nancial assets are
largely managed by Volvo Treasury and invested in the money and
capital markets. All investments must meet the requirements of low
credit risk and high liquidity. According to Volvo’s credit policy, coun-
terparties for investments and derivative transactions should have a
rating of A or better from one of the well-established credit rating
institutions.
The use of derivatives involves a counterparty risk, in that a poten-
tial gain will not be realized if the counterparty fails to fulfi ll its part
of the contract. To reduce the exposure, master netting agreements
are signed, wherever possible, with the counterparty in question.
With future, counterparty risk exposure is limited through daily or
monthly cash transfers corresponding to the value change of open
contracts. The estimated gross exposure to counterparty risk relat-
ing to futures, interest-rate swaps and interest-rate forward con-
tracts, options and commodities contracts amounted at December
31, 2006, to 1,158 (891), 2,621 (2,468), 78 (51) and 25 (54).
Over and above the credit risk of derivatives, there is also credit
risk in accounts receivable and receivables within Volvo’s sale
fi n a ncing operations.
Liquidity risks
Volvo assures itself of sound fi n ancial preparedness by always keep-
ing a certain percentage of its sales in liquid assets. A sound bal-
ance between short- and long-term borrowing, as well as borrowing
preparedness in the form of overdraft facilities, should cover long-
term fi n ancing needs.