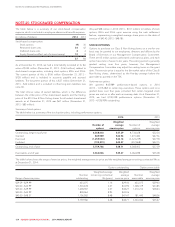
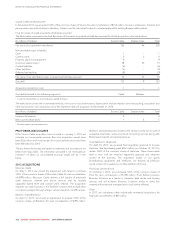
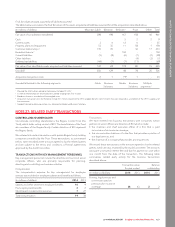
Rogers 2014 Annual Report Download - page 137
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 137 of the 2014 Rogers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Machine to Machine (M2M): Refers to the
inter-connection of physical devices or objects
wirelessly that are seamlessly integrated into
an information network to become active
participants in business processes. Services
are available to interact with these ‘smart
objects’ over the Internet, query and change
their state and to capture any information
associated with them.
Near-net: Customer location(s) adjacent
to network infrastructure allowing
connectivity to the premises to be
extended with relative ease.
Off-net: Customer location(s) where network
infrastructure is not readily available,
necessitating the use of a third-party leased
access for connectivity to the premises.
On-net: Customer location(s) where
network infrastructure is in place to provide
connectivity to the premises without further
builds or 3rd party leases. An on-net
customer can be readily provisioned.
OTT (Over-The-Top): Audio, visual or
alternative media distributed via the
Internet or other non-traditional media.
Penetration: Refers to the degree to which
a product or service has been sold into or
adopted by the base of potential customers
or subscribers in a given geographic area.
POPs (Persons of Population): A wireless
industry term for population or number of
potential subscribers in a market, a measure
of the market size. A POP refers to one
person living in a population area, which,
in whole or in substantial part, is included
in the coverage areas.
Postpaid: A conventional method of payment
for wireless service where a subscriber pays a
fixed monthly fee for a significant portion of
services and usage in arrears, subsequent to
consuming the services. The fees are usually
arranged on a term contract basis.
Prepaid: A method of payment for wireless
service that allows a subscriber to prepay for
a set amount of airtime in advance of actual
usage. Generally, a subscriber’s prepaid
account is debited at the time of usage so
that actual usage cannot exceed the prepaid
amount until an additional prepayment is
made.
PVR (Personal Video Recorder): A consumer
electronics device or application software
that records video in a digital format.
The term includes set-top boxes with
direct to disk recording facility, which
enables video capture and playback to
and from a hard disk.
Set-Top Box: A stand-alone analog or
digital device that receives and decodes
programming so that it may be displayed
on a television. Set-top boxes may be used
to receive broadcast, cable, and satellite
programming.
Spectrum: A term generally applied to
electromagnetic radio frequencies used in
the transmission of sound, data, and video.
Various portions of spectrum are designated
for cellular service, television, FM radio, and
satellite transmissions or other.
SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand):
Offers, for a monthly charge, access to specific
programming with unlimited viewing on an
on-demand basis.
TSU (Total Service Unit or Cable TSU):
In the cable TV industry includes television
subscribers, Internet subscribers and cable
telephony subscribers. A subscriber who takes
television and Internet is counted as two TSUs.
A subscriber who takes television, Internet and
cable telephony is counted as three TSUs, etc.
VOD (Video on Demand): A cable service
that allows a customer to select and order
movies and shows at any time from a library of
thousands of titles. Viewers can then pause,
fast forward or rewind the content.
VoIP (Voice over IP): The technology used
to transmit real time voice conversations
in data packets over a data network using
Internet Protocol. Such data networks include
telephone company networks, cable TV
networks, wireless networks, corporate
intranets and the Internet.
VoLTE (Voice over LTE): A platform to provide
voice services to wireless customers over
LTE wireless networks. The LTE standard
only supports packet switching as it is all-IP
technology based. Voice calls in GSM are
circuit switched, so with the adoption of
LTE, carriers are required to re-engineer their
voice call network, while providing continuity
for traditional circuit-switched networks on
2G and 3G networks. VoLTE provides greatly
enhanced quality of experience for voice calls.
Wi-Fi: The commercial name for a networking
technology standard for wireless local area
networks that essentially provide the same
connectivity as wired networks, but at lower
speeds. Wi-Fi allows any user with a Wi-Fi
enabled device to connect to a wireless
access point.
Helpful Links
Canadian Radio-Television and
Telecommunications Commission (CRTC)
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications
Commission (CRTC) is an independent agency of the
federal government responsible for regulating Canada’s
broadcasting and telecommunications systems. They
report to Parliament through the Minister of Canadian
Heritage. www.crtc.gc.ca
Industry Canada
Industry Canada is a ministry of the federal government
whose mission is to foster a growing, competitive,
knowledge-based Canadian economy. They also work
with Canadians throughout the economy and in all parts
of the country to improve conditions for investment,
improve Canada’s innovation performance, increase
Canada’s share of global trade and build a fair, efficient
and competitive marketplace. Program areas include
developing industry and technology capability, fostering
scientific research, setting telecommunications policy,
promoting investment and trade, promoting tourism
and small business development, and setting rules
and services that support the effective operation of the
marketplace. www.ic.gc.ca
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
is an independent United States government agency.
The FCC was established by the Communications
Act of 1934 and is charged with regulating interstate and
international communications by radio, television, wire,
satellite and cable. The FCC’s jurisdiction covers the 50
states, the District of Columbia, and U.S. possessions.
www.fcc.gov
Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association
(CWTA)
The Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association
(CWTA) is the industry trade organization and authority
on wireless issues, developments and trends in Canada.
It represents cellular, PCS, messaging, mobile radio,
fixed wireless and mobile satellite carriers as well as
companies that develop and produce products and
services for the industry. www.cwta.ca
CTIA The Wireless Association
CTIA The Wireless Association is an international
nonprofit membership organization founded in 1984,
representing all sectors of wireless communications
– cellular, personal communication services and
enhanced specialized mobile radio. As an organization,
it represents service providers, manufacturers,
wireless data and Internet companies, as well as other
contributors to the wireless universe. CTIA advocates
on their behalf before the Executive Branch, the Federal
Communications Commission, Congress, and state
regulatory and legislative bodies. www.ctia.org
GSM Association (GSMA)
Founded in 1987, The GSM Association (GSMA)
is a global trade association representing more
than 750 GSM mobile phone operators across
218 territories and countries of the world. In addition,
more than 180 manufacturers and suppliers support
the Association’s initiatives as associate members.
The primary goals of the GSMA are to ensure mobile
phones and wireless services interoperate globally.
www.gsmworld.com
For a more comprehensive
glossary of industry and
technology terms, go to
rogers.com/glossary
2014 ANNUAL REPORT ROGERS COMMUNICATIONS INC. 133
GLOSSARY