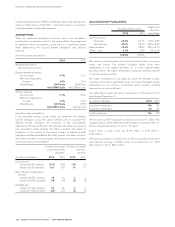
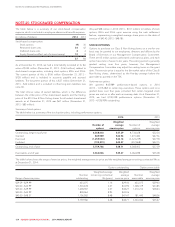
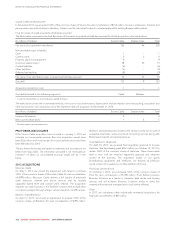
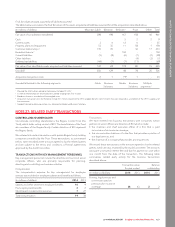
Rogers 2014 Annual Report Download - page 136
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 136 of the 2014 Rogers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Glossary of Selected Industry Terms
and Helpful Links
3.5G (Enhanced Third Generation Cellular
Wireless): Refers to evolutionary upgrades to
3G services that provide significantly enhanced
broadband wireless data performance to enable
multi-megabit data speeds. The key 3.5G
technologies in North America are High-Speed
Packet Access (HSPA) and CDMA EV-DO.
4G (Fourth Generation): A technology that
offers increased voice, video and multimedia
capabilities; a higher network capacity; improved
spectral efficiency; and high-speed data rates
over current 3G benchmarks.
4K – Ultra-High Definition Video: Denotes a
very specific television display resolution of
4096 x 2160. Today’s 1920 x 1080 resolution
full HD televisions present an image of around
2 megapixels, while the 4K generation of
screens delivers an 8 megapixel image.
ARPU (Average Revenue per User): Average
revenue per user, or subscriber, expressed as a
dollar rate per month for a given measurement
period. Predominantly used in the wireless
and cable industries to describe the revenue
generated per customer per month. ARPU is
an indicator of a wireless or cable business’
operating performance.
AWS (Advanced Wireless Services): The wireless
telecommunications spectrum band that is used
for wireless voice, data, messaging services and
multimedia.
Bandwidth: Bandwidth can have two different
meanings: (1) a band or block of radio
frequencies measured in cycles per second,
or Hertz; (2) an amount or unit of capacity in
a telecommunications transmission network.
In general terms, bandwidth is the available
space to carry a signal: the greater the bandwidth,
the greater the information-carrying capacity.
Bps (Bits per Second): A measurement of data
transmission speed used for measuring the
amount of data that is transferred in a second
between two telecommunications points or within
network devices. Kbps (kilobits per second) is
thousands of bps; Mbps (megabits per second)
is millions of bps; Gbps (gigabits per second)
is billions of bps; and Tbps (terabits per second)
is trillions of bps.
Broadband: High-speed transmission. The term
is commonly used to refer to communications
services which allow transmission of voice, data,
and video simultaneously at rates of 1.544Mbps
and above.
Cable Telephony (Phone): The transmission
of real time voice communications over a cable
network.
Churn: The term used to describe the disconnect
rate of customers to a telecommunications
service. Usually expressed as a percentage and
calculated as the number of subscriber units
disconnecting in a one month period divided
by the average number of units on the network.
It is a measure of customer turnover and is often
at least partially reflective of service quality and
competitive intensity.
CLEC (Competitive Local Exchange Carrier):
A telecommunications provider company that
competes with other, already established carriers,
generally the incumbent local exchange carrier
(ILEC).
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is a
synonym for distributed computing, and enables
the ability to run a program or application on
many connected computers at the same time.
CRTC (Canadian Radio-television and
Telecommunications Commission): The federal
regulator for radio and television broadcasters,
and cable-TV and telecommunications companies
in Canada.
Data Centre: A data centre is a facility used
to house computer systems and associated
components, such as telecommunications and
storage systems. It generally includes redundant
or backup power supplies, redundant data
communications connections, environmental
controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression)
and security devices.
DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface
Specification): A non-proprietary industry
standard developed by Cable Labs that allows
for equipment interoperability from the headend
to the CPE (located at the home). The latest
version (DOCSIS 3.0) enables bonding of multiple
channels to allow for +100Mbps transmission
speeds depending upon how many channels are
bonded together.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line): A family of
broadband technologies that offers always-
on, high-bandwidth (usually asymmetrical)
transmission over an existing twisted-pair copper
telephone line. DSL shares the same phone line
as the telephone service, but it uses a different
part of the phone line’s bandwidth.
Fibre-Optics: A method for the transmission
of information (voice, video or data) in which
light is modulated and transmitted over hair-thin
filaments of glass called fibre-optic cables.
The bandwidth capacity of fibre-optic cable is
much greater than that of copper wire and light
can travel relatively long distances through glass
without the need for amplification.
FTTH (Fibre-To-The-Home): Represents fibre
optic cable that reaches the boundary of the living
space, such as a box on the outside wall of a home.
GSM (Global System for Mobile): GSM is a
TDMA-based technology and a member of
the so-called “second generation” (2G) family
of mobile protocols that is deployed widely
around the world, especially at the 850, 900,
1800, and 1900 MHz frequency bands.
Homes Passed: Total number of homes which
have the potential for being connected to a
cable system in a defined geographic area.
Hosting (Web Hosting): The business of housing,
serving and maintaining files for one or more
websites or email accounts. Using a hosting
service allows many companies to share the cost
of a high-speed Internet connection for serving
files, as well as other Internet infrastructure and
management costs.
Hotspot: The Wi-Fi wireless access point in a
public place such as a café, train station, airport,
commercial office property or conference centre.
HSPA (High Speed Packet Access): HSPA is an
IP-based packet-data enhancement technology
that provides high-speed broadband packet data
services over 3G networks. HSPA+ provides high-
speed broadband packet data services at even
faster speeds than HSPA over 4G networks.
HUP (Hardware Upgrade): When an existing
wireless customer upgrades to a new wireless
device this is referred to as a HUP or Hardware
UPgrade.
ILEC (Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier): The
dominant telecommunications company providing
local telephone service in a given geographic area
when competition began. Typically an ILEC
is the traditional phone company and original
local exchange carrier in a given market.
Industry Canada: The Canadian federal
government department responsible for, amongst
other things, the regulation, management and
allocation of radio spectrum and establishing
technical requirements for various wireless
systems.
IP (Internet Protocol): The packet-based computer
network protocol that all machines on the Internet
must know so that they can communicate with one
another. IP is basically a set of data switching and
routing rules that specify how information is cut
up into packets and how they are addressed for
delivery between computers.
IPTV (Internet Protocol Television): A system
where a digital television signal is delivered using
Internet Protocol. Unlike broadcasting, viewers
receive only the stream of content they have
requested (by surfing channels or ordering video
on demand).
ISP (Internet Service Provider): A provider of
Internet access service to consumers and/or
businesses.
LTE (Long-Term Evolution): A fourth generation
cellular wireless technology (also known as 4G)
which has evolved and enhanced the HSPA+
mobile phone standards. LTE improves spectral
efficiency, lowers costs, improves services and,
most importantly, allows for higher data rates.
LTE technology is designed to deliver at speeds
up to 150Mbps with further increases over time.
LTE Advanced: A mobile communication standard
which represents a major enhancement of the
Long Term Evolution (LTE) standard. With a peak
data rate of 1 Gbps, LTE Advanced also offers
faster switching between power states and
improved performance at the cell edge.
132 ROGERS COMMUNICATIONS INC. 2014 ANNUAL REPORT