MasterCard 2008 Annual Report Download - page 96
Download and view the complete annual report
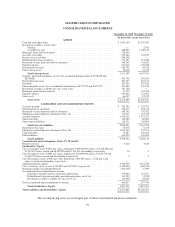
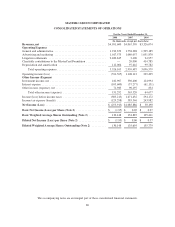
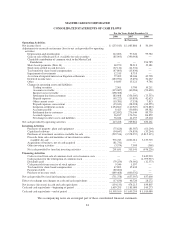
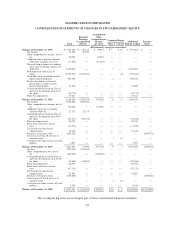
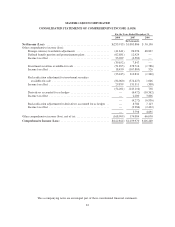
Please find page 96 of the 2008 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.MASTERCARD INCORPORATED
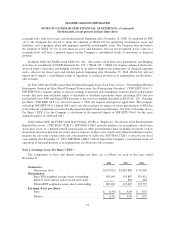
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
(In thousands, except percent and per share data)
should be considered when measuring fair value and how the use of market quotes should be considered when
assessing the relevance of observable and unobservable data available to measure fair value. The Company has
incorporated the considerations of FSP 157-3 in its assessment of the fair value of its ARS as of December 31, 2008.
Also effective January 1, 2008, the Company adopted SFAS No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial
Assets and Financial Liabilities Including an Amendment of FASB Statement No. 115” (“SFAS 159”). SFAS
159 permits entities to choose to measure many financial instruments and certain other items at fair value.
Election of the fair value option is irrevocable and is applied on a contract-by-contract basis. The Company has
elected not to apply the fair value option to its eligible financial assets and liabilities, and accordingly, the
adoption of SFAS 159 had no financial statement impact.
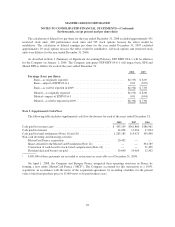
The Company classifies debt securities as held-to-maturity or available-for-sale and classifies equity
securities as available-for-sale or trading. Available-for-sale securities that are available to meet the Company’s
current operational needs are classified as current assets. Available-for-sale securities that are not available to
meet the Company’s current operational needs are classified as non-current assets.
Debt securities are classified as held-to-maturity when the Company has the intent and ability to hold the
debt securities to maturity and are stated at amortized cost. Debt securities not classified as held-to-maturity are
classified as available-for-sale and are carried at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses, net of applicable
taxes, recorded as a separate component of other comprehensive income (loss) on the consolidated statements of
comprehensive income (loss). Net realized gains and losses on debt securities are recognized in investment
income on the consolidated statements of operations.
Equity securities bought and held primarily for sale in the near term are classified as trading and are carried
at fair value. Net realized and unrealized gains and losses on trading securities are recognized in investment
income on the consolidated statements of operations. Equity securities not classified as trading are classified as
available-for-sale and are carried at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses, net of applicable taxes, recorded
as a separate component of other comprehensive income (loss) on the consolidated statements of comprehensive
income (loss). Net realized gains and losses on available-for-sale equity securities are recognized in investment
income on the consolidated statements of operations. The specific identification method is used to determine
realized gains and losses.
Held-to-maturity and available-for-sale investments are evaluated for other than temporary impairment on
an ongoing basis in accordance with SFAS No. 115, “Accounting for Certain Investments in Debt and Equity
Securities”. If an investment is determined to be other than temporarily impaired, realized losses are recognized
in investment income on the consolidated statements of operations. See Note 4 (Investment Securities) for
additional information on the Company’s investment securities.
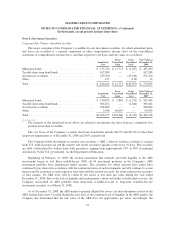
Settlement due from/due to customers—The Company operates systems for clearing and settling payment
transactions among MasterCard International members. Net settlements are generally cleared daily among
members through settlement cash accounts by wire transfer or other bank clearing means. However, some
transactions may not settle until subsequent business days, resulting in amounts due from and due to MasterCard
International members.
Restricted security deposits held for MasterCard International members—MasterCard requires and holds
cash deposits and certificates of deposits from certain members of MasterCard International as collateral for
settlement of their transactions. These assets are fully offset by corresponding liabilities included on the
consolidated balance sheets. However, the majority of collateral for settlement is typically in the form of standby
letters of credit and bank guarantees which are not recorded on the balance sheet.
86