MasterCard 2008 Annual Report Download - page 84
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 84 of the 2008 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
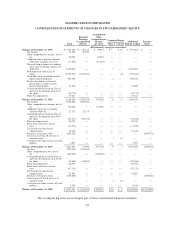
measure the fair value of plan assets and concentrations of credit risk. FSP SFAS 132R-1 is effective for fiscal
years ending after December 15, 2009. FSP SFAS 132R-1 will not impact the Company’s consolidated results of
operations or financial position as its requirements are disclosure-only in nature.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Market risk is the potential for economic losses to be incurred on market risk sensitive instruments arising
from adverse changes in market factors such as interest rates, foreign currency exchange rates and equity price
risk. We have limited exposure to market risk from changes in interest rates, foreign exchange rates and equity
price risk. Management establishes and oversees the implementation of policies, which have been approved by
the Board of Directors, governing our funding, investments and use of derivative financial instruments. We
monitor risk exposures on an ongoing basis. There were no material changes in our market risk exposures at
December 31, 2008 as compared to December 31, 2007.
Foreign Exchange Risk
We enter into forward exchange contracts to minimize risk associated with anticipated receipts and
disbursements which are either transacted in a non-functional currency or valued based on a currency other than
our functional currencies. We also enter into contracts to offset possible changes in value due to foreign
exchange fluctuations of assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies. The objective of this activity is
to reduce our exposure to transaction gains and losses resulting from fluctuations of foreign currencies against
our functional currencies, principally the U.S. dollar and euro. The terms of the forward currency contracts are
generally less than 18 months.
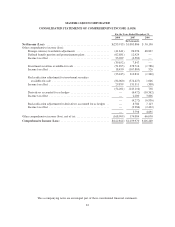
U.S. Dollar Functional Currency
(In millions)
December 31, 2008 December 31, 2007
Notional
Estimated
Fair Value Notional
Estimated
Fair Value
Commitments to purchase foreign currency ..................... $293 $22 $40 $—
Commitments to sell foreign currency .......................... 154 12 22 —
Euro Functional Currency
(In millions)
December 31, 2008 December 31, 2007
Notional
Estimated
Fair Value Notional
Estimated
Fair Value
Commitments to sell foreign currency .......................... $66 $— $50 $—
Our settlement activities are subject to foreign exchange risk resulting from foreign exchange rate
fluctuations. This risk is limited to the typical one business day timeframe between setting the foreign exchange
rates and clearing the financial transactions and by confining the supported settlement currencies to the U.S.
dollar or one of 16 other transaction currencies. The remaining 143 transaction currencies are settled in one of the
supported settlement currencies or require local settlement netting arrangements that minimize our foreign
exchange exposure.
74