IBM 2005 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2005 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
NotestoConsolidatedFinancialStatements
INTERNATIONALBUSINESSMACHINESCORPORATION ANDSUBSIDIARYCOMPANIES
_71
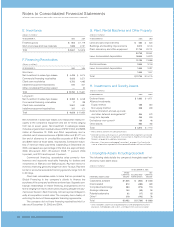
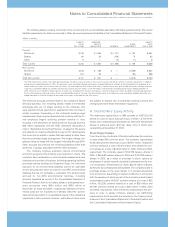
Post-SwapBorrowing(long-termdebt, includingcurrentportion)
(Dollarsinmillions)
2005 2004
ATDECEMBER31: AMOUNT AVERAGERATE AMOUNT AVERAGERATE
Fixedratedebt $«««8,099 «4.84% $«««9,112 «4.13%
Floatingratedebt* «10,314 «4.82% «««9,324 «3.22%
Total $«18,413 « $«18,436 «««
* Includes$7,811 millionin2005and $8,326 millionin2004ofnotionallong-terminterestrateswapsthateffectivelyconvertthefixed-ratedebtintofloating-ratedebt.(Seenote
L,“DerivativesandHedgingTransactions,”onpages 71 to74).
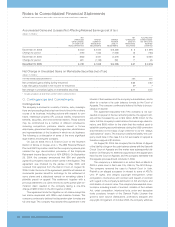
Pre-swap annual contractual maturities of long-term debt out-
standing atDecember31,2005,are asfollows:
(Dollarsinmillions)
2006 $«««3,013
2007 2,843
2008 1,485
2009 2,195
2010 1,690
2011 andbeyond 6,961
Total $«18,187
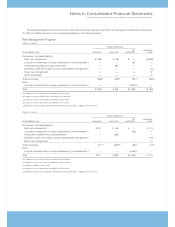
InterestonDebt
(Dollarsinmillions)
FORTHEYEARENDEDDECEMBER31: 2005 2004 2003
CostofGlobalFinancing $«525 $«428 $«503
Interestexpense 220 139 145
Interestcapitalized 16 415
Totalinterest ondebt $«761 $«571 $«663
Refer to the related discussion on page 97 in note W,
“SegmentInformation,” fortotalinterestexpenseoftheGlobal
Financing segment. See note L, “Derivatives and Hedging
Transactions,” onpages 71 to74 foradiscussionoftheuseof
currencyand interestrateswaps in thecompany’s debt risk
managementprogram.
LinesofCredit
OnMay27,2004,thecompanycompletedtherenegotiationofa
new$10billion 5-yearCreditAgreement with JP Morgan Chase
Bank,asAdministrativeAgent,andCitibank,N.A.,asSyndication
Agent,replacingcreditagreementsof$8billion(5-year)and$2
billion (364 day). The total expense recorded by the company
related to these facilities was $8.9 million for the years ended
December31,2005and2004, and$7.8 millionfortheyear ended
December 31, 2003. The new facility is irrevocable unless the
companyisin breachofcovenants, includinginterestcoverage
ratios,orifitcommitsanevent ofdefault,suchasfailingtopay
any amount due under this agreement. The company believes
that circumstances that might give rise to a breach of these
covenants or an event of default, as specified in these agree-
ments,areremote.Thecompany’s otherlinesof credit, most of
whichareuncommitted,totaled$10,057 millionand$9,041 million
atDecember31,2005 and2004,respectively.Interestratesand
other terms of borrowing under these lines of credit vary from
countrytocountry,dependingonlocalmarketconditions.
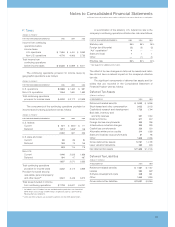
(Dollarsinmillions)
ATDECEMBER31: 2005 2004
Unusedlines:
Fromthecommitted
globalcreditfacility $«««9,913 $«««9,804
Fromothercommittedand
uncommittedlines 6,781 6,477
Totalunusedlinesofcredit $«16,694 $«16,281
L.DerivativesandHedgingTransactions
Thecompanyoperatesinmultiplefunctionalcurrenciesandisa
significantlenderandborrowerintheglobalmarkets.Inthenor-
malcourseofbusiness,thecompanyisexposedtotheimpactof
interestratechangesandforeigncurrencyfluctuations,andtoa
lesser extent equity price changes and client credit risk. The
companylimitstheserisksbyfollowingestablishedriskmanage-
mentpoliciesandprocedures,including theuseof derivatives,
and,wherecost-effective,financingwithdebtinthecurrenciesin
which assets are denominated. For interest rate exposures,
derivativesareusedtoalignratemovementsbetweentheinter-
estratesassociatedwiththecompany’sleaseandotherfinancial
assetsandtheinterestratesassociatedwithitsfinancingdebt.
Derivativesarealsousedtomanagetherelatedcostofdebt.For
foreign currency exposures, derivatives are used to limit the
effectsofforeignexchangeratefluctuationsonfinancialresults.
Asaresultofthecompany’suseofderivativeinstruments,
the company is exposed to the risk that counterparties to
derivativecontractswillfailtomeettheircontractualobligations.
To mitigate the counterparty credit risk, the company has a
policy of only entering into contracts with carefully selected
majorfinancial institutions basedupontheir creditratings and
other factors, and maintains strict dollar and term limits that
correspond to the institution’s credit rating. The company’s
establishedpoliciesandproceduresformitigatingcreditriskon
principaltransactionsincludereviewingandestablishinglimits
forcreditexposureand continually assessingthecreditworthi-
nessofcounterparties.Masteragreementswithcounterparties
include master netting arrangements as further mitigation of
creditexposure to counterparties. These arrangementspermit