IBM 2005 Annual Report Download - page 22
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 22 of the 2005 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ManagementDiscussion
INTERNATIONALBUSINESSMACHINESCORPORATION ANDSUBSIDIARYCOMPANIES
_21
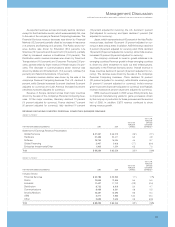
Global Asset Recovery Services—an operation of Global
Financing that restores end-of-lease personal computers and
otherITequipmentforresale.
KeyBusinessDrivers
The following are some of the key drivers of the com-
pany’sbusiness.
ECONOMIC ENVIRONMENT AND CORPORATE
SPENDING BUDGETS
Ifoveralldemandforsystems,softwareandserviceschanges,
whetherduetogeneraleconomicconditionsorashiftincorpo-
rate buying patterns, sales performance could be impacted.
IBM’sdiverseportfolioofproductsandofferingsisdesignedto
gainmarketshareinstrongandweakeconomicclimates.The
companyaccomplishesthisbynotonlyhavingamixofofferings
with long-term cash and income streams, as well as cyclical
transaction-based sales, but also by continually developing
competitive products and solutions and effectively managing
a skilled resource base. IBM continues to transform itself to
take advantage of shifting demand trends, focusing on client-
or industry-specific solutions, business performance and
openstandards.
INTERNAL BUSINESS TRANSFORMATION AND
GLOBAL INTEGRATION INITIATIVES
IBM continues to drive greater productivity, flexibility and cost
savings by transforming and globally integrating its own busi-
nessprocessesandfunctions.In2005,thecompanyrealigned
its operations and organizational structure in Europe to give
sales and delivery teams greater authority, accountability and
flexibilitytomakedecisionsandtoexecutemoreeffectivelyon
behalf of our clients. Additionally, in 2005, many of the com-
pany’s corporate functions—such as Legal, Finance, Human
Resources, Information Technology, and Real Estate Site
Operations—which had been previouslyreplicatedfor manyof
theindividualcountrieswhereIBMoperateswereintegratedso
thattheycouldbemanagedandtheirresourcesoptimizedona
globalscale.Inadditionto eliminating redundanciesandover-
head structures to drive productivity, this integration improved
IBM’scapacitytoinnovatebyprovidinggreaterclarityofkeypri-
oritiesaroundsharedgoalsandobjectivesand led toasharper
focus for the company on learning, development and knowl-
edgesharing.
INNOVATION INITIATIVES
IBM invests to improve its ability to help its clients innovate.
Investmentmayoccurin the researchanddevelopmentof new
productsandservices,aswellasintheestablishmentofnewcol-
laborative and co-creation relationships with developers, other
companies, and other institutions. To deliver value that helps
clients differentiate themselves for competitive advantage, IBM
hasbeen moving away fromcommoditizedcategories of theIT
industryandintoareasinwhichitcandifferentiateitselfthrough
innovation and by leveraging its investments in R&D. Examples
includeIBM’sleadershippositioninthedesignandfabricationof
ASICs;thedesignofsmaller,fasterandenergy-efficientsemicon-
ductor devices; the design of “grid” computing networks that
allow computers to share processing power; the transformation
andintegrationofbusinessprocesses;andthecompany’sefforts
toadvanceopentechnologystandardsandtoengagewithgov-
ernments,academia,thinktanksandnongovernmentalorganiza-
tionsonemergingtrendsintechnology,societyandculture.Inthe
highlycompetitiveITindustry,withlargediversifiedcompetitors,
as well as smaller and nimble single-technology competitors,
IBM’s ability to continue its cutting-edge innovation is critical to
maintaining and increasing market share. IBM is managing this
riskbymorecloselylinkingitsR&Dorganizations toindustry-spe-
cific and client-specific needs, as discussed in “Description of
Business—IBMWorldwideOrganizations” onpages19to21.
OPEN STANDARDS
Thebroadadoptionofopenstandardsisessentialtothecom-
puting model for an on demand business and is a significant
driver of collaborative innovation across all industries. Without
interoperability among all manner of computing platforms, the
integration of any client’s internal systems, applications and
processes remains a monumental and expensive task. The
broad-based acceptance of open standards—rather than
closed, proprietary architectures—also allows the computing
infrastructuretomoreeasilyabsorb(andthusbenefitfrom)new
technicalinnovations.IBMiscommittedtofosteringopenstan-
dards because they are vital to the On Demand Operating
Environment,andbecausetheiracceptancewillexpandgrowth
opportunitiesacrosstheentirebusinessservicesandITindus-
try.ThereareanumberofcompetitorsintheITindustrywithsig-
nificantresourcesandinvestmentswhoarecommittedtoclosed
andproprietaryplatformsasawaytolock clients intoaparticu-
lararchitecture.Thiscompetitionwillresultinincreasedpricing
pressure and/or IP claims and proceedings. IBM’s support of
openstandardsisevidencedbytheenablingofitsproductsto
supportopenstandardssuchasLinux,andthedevelopmentof
Rational software development tools, which can be used to
developandupgrade other companies’ softwareproducts.
INVESTING IN GROWTH OPPORTUNITIES
Thecompanyiscontinuingtorefocusitsbusinessonthehigher
value segments of enterprise computing—providing technology
and transformation services to clients’ businesses. Consistent
withthatfocus,thecompanycontinuestosignificantlyinvestin
growth opportunities asawaytodriverevenuegrowthandmar-
ket share gains. Areas of investment include strategic acquisi-
tions, primarily in software and services, focused client- and
industry-specific solutions, BPTS, keytechnologies and emerg-
inggrowthcountriessuchasChina,Russia,IndiaandBrazil.