Travelers 2006 Annual Report Download - page 142
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 142 of the 2006 Travelers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
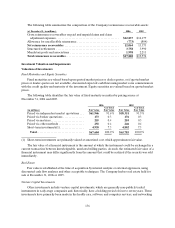 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285
 |
 |
130
and attachment point of coverage. The uncertainty surrounding reserves for small, commercial insureds is
typically less than the uncertainty for large commercial or financial institutions. The high frequency, low
severity nature of small commercial fidelity losses provides for stability in loss estimates whereas, the low
frequency, high severity nature of losses for large insureds results in a wider rangeof ultimate loss
outcomes. Actuarial techniques that rely on a stable pattern of loss development are generally not
applicable to low frequency, high severity policies.
Surety has certain components that are generally considered short tail coverages with short reporting
lags, although large individual construction and commercial surety contracts can result in a long settlement
tail, based onthe length and complexity of the construction project or commercial transaction being
insured. (Large construction projects can take many years to complete.) The frequency of losses in surety
correlates with economic cycles as the primary cause of surety loss is the inability to perform financially.
The volatility of surety losses is generally related to the type of business performed by the insured, the type
of bonded obligation, the amount of limit exposed to loss and the amount of assets available to the insurer
to mitigate losses, such as unbilled contract funds, collateral, first and thirdparty indemnity, and other
security positions of an insured’s assets. Certain classes of surety claims are very high severity, low
frequency in nature. These can include large construction contractors involved with one or multiple large,
complex projects as well as certain large commercial surety exposures. Other claim factors affecting reserve
variability of surety include litigation related to amounts owed by and due the insured (e.g., salvage and
subrogation efforts) and the results of financial restructuring of an insured.
Examples of common risk factors, or perceptions thereof, that could change and, thus, affect the
required fidelity and surety reserves (beyond those included in the general discussion section) include:
Fidelity risk factors
Type of business of insured
Policy limit and attachment points
Third-party claims
Coverage litigation
Complexity of claims
Growth in insureds’ operations
Surety risk factors
Economic trends, including the general level of construction activity
Concentration of reserves in a relatively few large claims
Type of business insured
Type of obligation insured
Cumulative limits of liability for insured
Assets available to mitigate loss
Defective workmanship/latent defects
Financial strategy of insured
Changes in statutory obligations
Geographic spread of business
Fidelity and Surety book of business risk factors
Changes in policy provisions (e.g., deductibles, limits, endorsements)
Changes in underwriting standards
Unanticipated changes in risk factors can affect reserves. As an indicator of the causal effect that a
change in one or more risk factors could have on reserves for fidelity and surety, a 1% increase (decrease)
in incremental paid loss development for each future calendar year could result in a 1.2% increase
(decrease) in loss reserves.
