The Hartford 2009 Annual Report Download - page 191
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 191 of the 2009 The Hartford annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.THE HARTFORD FINANCIAL SERVICES GROUP, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
F-42
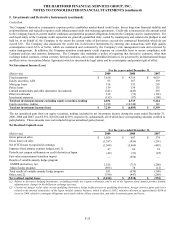
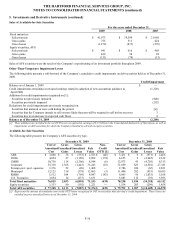
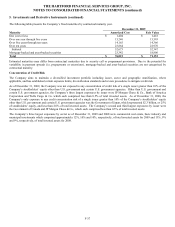
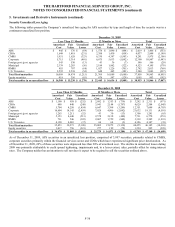
5. Investments and Derivative Instruments (continued)
Non-qualifying strategies
Interest rate swaps, caps, floors, and futures
The Company uses interest rate swaps, caps, floors, and futures to manage duration between assets and liabilities in certain investment
portfolios. In addition, the Company enters into interest rate swaps to terminate existing swaps, thereby offsetting the changes in value
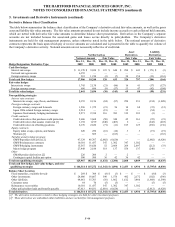
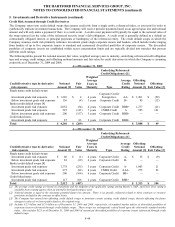
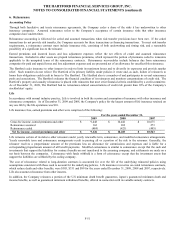
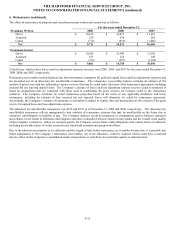
of the original swap. As of December 31, 2009 and 2008, the notional amount of interest rate swaps in offsetting relationships was $7.3
billion and $6.8 billion, respectively.
Foreign currency swap and forwards
The Company enters into foreign currency swaps and forwards to convert the foreign currency exposures to U.S. dollars in certain of its
foreign denominated fixed maturity investments. The Company also enters into foreign currency forward contracts that convert Euros
to Yen in order to economically hedge the foreign currency risk associated with certain assumed Japanese variable annuity products.
Japan 3Win related foreign currency swaps
During the first quarter of 2009, the Company entered into foreign currency swaps to hedge the foreign currency exposure related to the
Japan 3Win product guaranteed minimum income benefit (“GMIB”) fixed liability payments.
Japanese fixed annuity hedging instruments
The Company enters into currency rate swaps and forwards to mitigate the foreign currency exchange rate and Yen interest rate
exposures associated with the Yen denominated individual fixed annuity product.
Credit derivatives that purchase credit protection
Credit default swaps are used to purchase credit protection on an individual entity or referenced index to economically hedge against
default risk and credit-related changes in value on fixed maturity securities. These contracts require the Company to pay a periodic fee
in exchange for compensation from the counterparty should the referenced security issuers experience a credit event, as defined in the
contract.
Credit derivatives that assume credit risk
Credit default swaps are used to assume credit risk related to an individual entity, referenced index, or asset pool, as a part of replication
transactions. These contracts entitle the Company to receive a periodic fee in exchange for an obligation to compensate the derivative
counterparty should the referenced security issuers experience a credit event, as defined in the contract. The Company is also exposed
to credit risk due to embedded derivatives associated with credit linked notes.
Credit derivatives in offsetting positions
The Company enters into credit default swaps to terminate existing credit default swaps, thereby offsetting the changes in value of the
original swap going forward.
Equity index swaps, options, and futures
The Company offers certain equity indexed products, which may contain an embedded derivative that requires bifurcation. The
Company enters into S&P index swaps, futures and options to economically hedge the equity volatility risk associated with these
embedded derivatives. In addition, the Company is exposed to bifurcated options embedded in certain fixed maturity investments.
Warrants
During the fourth quarter of 2008, the Company issued warrants to purchase the Company's Series C Non-Voting Contingent
Convertible Preferred Stock, which were required to be accounted for as a derivative liability at December 31, 2008. For further
discussion of Allianz SE's investment in The Hartford, see Note 21. As of March 31, 2009, the warrants were no longer required to be
accounted for as derivatives and were reclassified to equity.
GMWB product derivatives
The Company offers certain variable annuity products with a GMWB rider in the U.S. and formerly in the U.K. and Japan. The GMWB
is a bifurcated embedded derivative that provides the policyholder with a GRB if the account value is reduced to zero through a
combination of market declines and withdrawals. The GRB is generally equal to premiums less withdrawals. Certain contract
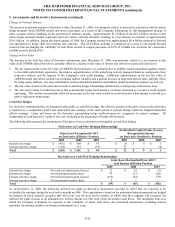
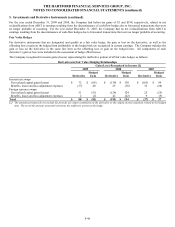
provisions can increase the GRB at contractholder election or after the passage of time. The notional value of the embedded derivative
is the GRB balance.