PNC Bank 2002 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2002 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.78
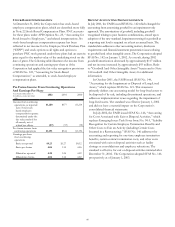
As required, effective January 1, 2001, the Corporation
implemented SFAS No. 133, “Accounting for Derivative
Instruments and Hedging Activities,” as amended. The
statement requires the Corporation to recognize all derivative
instruments at fair value as either assets or liabilities. Financial
derivatives are reported at fair value in other assets or other
liabilities. The accounting for changes in the fair value of a
derivative instrument depends on whether it has been
designated and qualifies as part of a hedging relationship. For
derivatives not designated as hedges, the gain or loss is
recognized in current earnings.
For those derivative instruments that are designated and
qualify as hedging instruments, the Corporation must
designate the hedging instrument, based on the exposure being
hedged, as either a fair value hedge, a cash flow hedge or a
hedge of a net investment in a foreign operation. The
Corporation has no derivatives that hedge the net investment
in a foreign operation.
For derivatives that are designated as fair value hedges (i.e.,
hedging the exposure to changes in the fair value of an asset
or a liability attributable to a particular risk), the gain or loss on
derivatives as well as the loss or gain on the hedged items are
recognized in current earnings. An adjustment to the hedged
item for the change in its fair value pertaining to the hedged
risk is included in its carrying value. For derivatives designated
as cash flow hedges (i.e., hedging the exposure to variability in
expected future cash flows), the effective portions of the gain
or loss on derivatives are reported as a component of
accumulated other comprehensive income and recognized in
earnings in the same period or periods during which the
hedged transaction affects earnings. Any remaining gain or
loss on these derivatives is recognized in current earnings. The
Corporation will discontinue hedge accounting prospectively
when it determines that the derivative is no longer an effective
hedge, the derivative expires or is sold, or management
discontinues the derivative’s hedge designation. In those
circumstances, amounts included in accumulated other
comprehensive income regarding a cash flow hedge are
recognized in earnings to match the earnings recognition
pattern of the hedged item (e.g., level yield amortization if
hedging an interest-bearing instrument). The Corporation
terminated no cash flow hedges in 2002 or 2001 due to a
determination that a forecasted transaction was no longer
likely to occur.
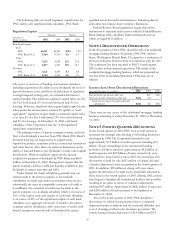
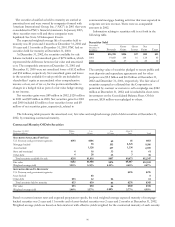
Fair Value Hedging Strategies
The Corporation enters into interest rate and total rate of
return swaps, caps, floors and interest rate futures derivative
contracts to hedge designated commercial mortgage loans held
for sale, securities available for sale, commercial loans, bank
notes, senior debt and subordinated debt for changes in fair
value primarily due to changes in interest rates. Adjustments
related to the ineffective portion of fair value hedging
instruments are recorded in interest income, interest expense
or noninterest income depending on the hedged item.
Cash Flow Hedging Strategy
The Corporation enters into interest rate swap contracts to
modify the interest rate characteristics of designated
commercial loans from variable to fixed in order to reduce the
impact of interest rate changes on future interest income. The
fair value of these derivatives is reported in other assets or
other liabilities and offset in accumulated other comprehensive
income for the effective portion of the derivatives. When the
hedged transaction culminates, any unrealized gains or losses
related to these swap contracts are removed from accumulated
other comprehensive income and are included in interest
income. Ineffectiveness of the strategy, as defined under SFAS
No. 133, if any, is reported in interest income.
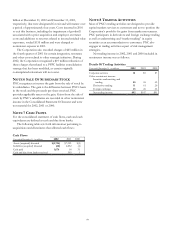
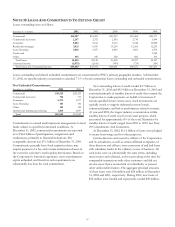
Customer And Other Derivatives
To accommodate customer needs, PNC also enters into
financial derivative transactions primarily consisting of interest
rate swaps, caps, floors and foreign exchange contracts.
Market risk exposure from customer positions is managed
through transactions with other dealers. The credit risk
associated with derivatives executed with customers is
essentially the same as that involved in extending loans and is
subject to normal credit policies. Collateral may be obtained
based on management’s assessment of the customer.
Additionally, the Corporation enters into other derivative
transactions for risk management purposes that are not
designated as accounting hedges, including credit default
swaps which are used to mitigate credit risk and lower the
required regulatory capital associated with commercial lending
activities. The positions of customer and other derivatives are
recorded at fair value and changes in value are included in
noninterest income.