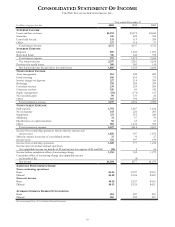
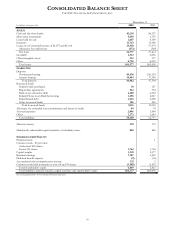
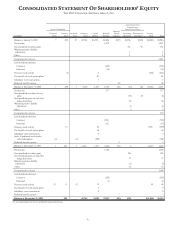
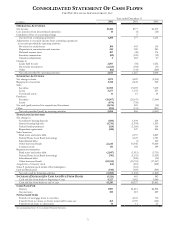
PNC Bank 2002 Annual Report Download - page 74
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 74 of the 2002 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
THE PNC FINANCIAL SERVICES GROUP, INC.
72
BUSINESS
The PNC Financial Services Group, Inc. (“Corporation” or
“PNC”) is one of the largest diversified financial services
companies in the United States, operating businesses engaged
in regional community banking; wholesale banking, including
corporate banking, real estate finance and asset-based lending;
wealth management; asset management and global fund
processing services. The Corporation provides certain
products and services nationally and others in PNC’s primary
geographic markets in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Delaware,
Ohio and Kentucky. The Corporation also provides certain
banking, asset management and global fund processing
services internationally. PNC is subject to intense competition
from other financial services companies and is subject to
regulation by various domestic and international authorities.
NOTE 1 ACCOUNTING POLICIES
BASIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT PRESENTATION
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of
PNC and its subsidiaries, most of which are wholly owned,
and certain general partnership interests. Such statements have
been prepared in accordance with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States of America (“generally
accepted accounting principles”). All significant intercompany
accounts and transactions have been eliminated. Certain prior-
period amounts have been reclassified to conform with the
current period presentation. These reclassifications did not
impact the Corporation’s consolidated financial condition or
results of operations. The consolidated financial statements
and notes to consolidated financial statements reflect the
residential mortgage banking business, which was sold on
January 31, 2001, in discontinued operations, unless otherwise
noted.
INVESTMENTS
PNC has interests in various types of investments. The
accounting for these investments is dependent on a number of
factors including, but not limited to, items such as
marketability of the investment, ownership interest, PNC’s
intent and the nature of the investment.
Venture capital investments, which include both direct
investments in companies and interests in limited partnerships,
are reported at estimated fair values. These estimates are based
upon available information and may not necessarily represent
amounts that will ultimately be realized through distribution,
sale or liquidation of the investment. The valuation procedures
applied to direct investments include valuation techniques
such as multiples of earnings before interest, taxes,
depreciation and amortization of the entity, independent
appraisals of the entity or the pricing used to value the entity
in a recent financing transaction. Limited partnership
investments are valued based on the financial statements
received from the general partner, an independent third party.
All venture capital investments are included in the
consolidated balance sheet under other assets. Changes in the
fair value of these assets are recognized in noninterest income.
Equity investments other than venture capital investments
are accounted for under one of the following methods:
• Marketable equity securities are accounted for at fair value
based on the securities’ quoted market price from a
national securities exchange. Those purchased with the
intention of recognizing short-term profits are placed in
the trading account, carried at market value and classified
as short-term investments. Gains and losses on trading
securities are included in noninterest income. Marketable
equity securities not classified as trading are designated as
securities available for sale and are carried at fair value
with unrealized gains and losses, net of income taxes,
reflected in accumulated other comprehensive income or
loss.
• Investments in nonmarketable equity securities are
recorded using the cost or equity methods of accounting.
The cost method is used for those investments in which
PNC does not have significant influence over the
investee. Under this method, there is no change to the
cost basis unless there is an other than temporary decline
in value, which results in an impairment charge.
Dividends received on cost investments are included in
noninterest income. The equity method is used for those
investments in which PNC can have significant influence
over the operations of the investee. Under the equity
method, PNC records its equity ownership share of the
net income or loss of the investee in noninterest income.
PNC records its nonmarketable equity securities in other
assets.
• Additionally, investments in limited partnerships are
accounted for under either the cost method or the equity
method as described above for nonmarketable equity
securities. The equity method is used if the limited
partner’s ownership interest in the partnership is greater
than 3% to 5%. For the remaining limited partnership
investments, the cost method is used. Limited partnership
investments are included in other assets.
Debt securities are classified as securities and carried at
amortized cost if management has the positive intent and
ability to hold the securities to maturity. Debt securities
purchased with the intention of recognizing short-term profits