PNC Bank 2002 Annual Report Download - page 58
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 58 of the 2002 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
56
The Corporation uses a variety of financial derivatives as
part of the overall asset and liability risk management process
to help manage interest rate, market and credit risk inherent in
the Corporation’s business activities. Substantially all such
instruments are used to manage risk related to changes in
interest rates. Interest rate and total rate of return swaps,
purchased interest rate caps and floors and futures contracts
are the primary instruments used by the Corporation for
interest rate risk management.
Interest rate swaps are agreements with a counterparty to
exchange periodic fixed and floating interest payments
calculated on a notional amount. The floating rate is based on
a money market index, primarily short-term LIBOR. Total rate
of return swaps are agreements with a counterparty to
exchange an interest rate payment for the total rate of return
on a specified reference index calculated on a notional
amount. Purchased interest rate caps and floors are
agreements where, for a fee, the counterparty agrees to pay the
Corporation the amount, if any, by which a specified market
interest rate exceeds or is less than a defined rate applied to a
notional amount, respectively. Interest rate futures contracts
are exchange-traded agreements to make or take delivery of a
financial instrument at an agreed upon price and are settled in
cash daily.
Financial derivatives involve, to varying degrees, interest
rate, market and credit risk. For interest rate swaps and total
rate of return swaps, caps and floors and futures contracts,
only periodic cash payments and, with respect to caps and
floors, premiums, are exchanged. Therefore, cash
requirements and exposure to credit risk are significantly less
than the notional value.
Not all elements of interest rate, market and credit risk are
addressed through the use of financial or other derivatives,
and such instruments may be ineffective for their intended
purposes due to unanticipated market characteristics among
other reasons.
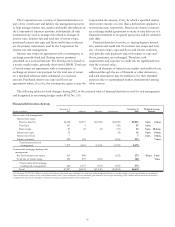
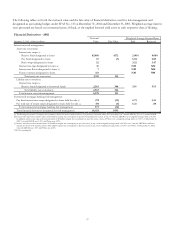
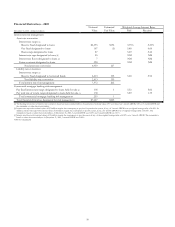
The following tables set forth changes, during 2002, in the notional value of financial derivatives used for risk management
and designated as accounting hedges under SFAS No. 133.
Financial Derivatives Activity
December 31 December 31 Weighted-Average
Dollars in millions 2001 Additions Maturities Terminations 2002 Maturity
Interest rate risk management
Interest rate swaps
Receive fixed (a) $6,748 $2,975 $(1,300) $(2,600) $5,823 3 yrs. 2 mos.
Pay fixed 107 5 (45) 67 4 yrs.
Basis swaps 87 45 (5) (75) 52 5 yrs. 10 mos.
Interest rate caps 25 (9) 16 4 yrs. 8 mos.
Interest rate floors 7 7 2 yrs. 3 mos.
Futures contracts 398 378 (463) 313 7 mos.
Total interest rate risk
management 7,372 3,403 (1,305) (3,192) 6,278
Commercial mortgage banking risk
mana
g
ement
Pay fixed interest rate swaps 105 800 (632) 273 10 yrs. 1 mo.
Total rate of return swaps 150 275 (325) 100 1 mo.
Total commercial mortgage
bankin
g
risk mana
g
ement 255 1,075 (325) (632) 373
Total $7,627 $4,478 $(1,630) $(3,824) $6,651
(a) On January 24, 2003, $1.2 billion of receive-fixed interest rate swaps were terminated. As cash flow hedge designated derivatives, unrealized gains or losses are classified as accumulated
other comprehensive income in the consolidated balance sheet. Upon termination, the net unrealized gains related to these swaps amounting to $34.5 million will be amortized from other
comprehensive income into earnings to match the earnings recognition pattern of the hedged items.