IBM 2009 Annual Report Download - page 96
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 96 of the 2009 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
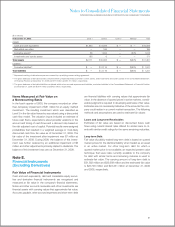
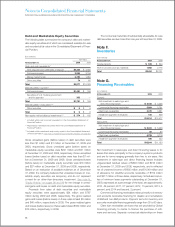
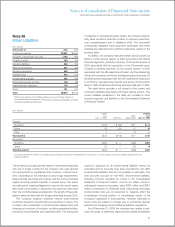
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARY COMPANIES
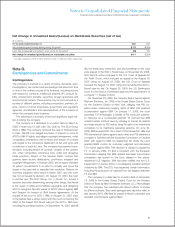
Foreign Exchange Risk
Long-Term Investments in Foreign Subsidiaries
(Net Investment)
A significant portion of the company’s foreign currency denomi-
nated debt portfolio is designated as a hedge of net investment
to reduce the volatility in equity caused by changes in foreign
currency exchange rates in the functional currency of major
foreign subsidiaries with respect to the U.S. dollar. The company
also uses cross-currency swaps and foreign exchange forward
contracts for this risk management purpose. At December 31,
2009, the total notional amount of derivative instruments desig-
nated as net investment hedges was $1.0 billion.
Anticipated Royalties and Cost Transactions
The company’s operations generate significant nonfunctional cur-
rency, third-party vendor payments and intercompany payments
for royalties and goods and services among the company’s non-
U.S. subsidiaries and with the parent company. In anticipation of
these foreign currency cash flows and in view of the volatility of
the currency markets, the company selectively employs foreign
exchange forward contracts to manage its currency risk. These
forward contracts are accounted for as cash flow hedges. The
maximum length of time over which the company is hedging its
exposure to the variability in future cash flows is approximately
four years. At December 31, 2009, the total notional amount of
forward contracts designated as cash flow hedges of forecasted
royalty and cost transactions was $18.7 billion with a weighted-
average remaining maturity of 1.3 years.
Foreign Currency Denominated Borrowings
The company is exposed to exchange rate volatility on foreign
currency denominated debt. To manage this risk, the company
employs cross-currency swaps to convert fixed-rate foreign
currency denominated debt to fixed-rate debt denominated in
the functional currency of the borrowing entity. These swaps
are accounted for as cash flow hedges. The maximum length
of time over which the company is hedging its exposure to the
variability in future cash flows is approximately five years. At
December 31, 2009, the total notional amount of cross-currency
swaps designated as cash flow hedges of foreign currency
denominated debt was $0.3 billion.
Subsidiary Cash and Foreign Currency
Asset/Liability Management
The company uses its Global Treasury Centers to manage the
cash of its subsidiaries. These centers principally use currency
swaps to convert cash flows in a cost-effective manner. In addi-
tion, the company uses foreign exchange forward contracts to
economically hedge, on a net basis, the foreign currency expo-
sure of a portion of the company’s nonfunctional currency assets
and liabilities. The terms of these forward and swap contracts
are generally less than two years. The changes in the fair values
of these contracts and of the underlying exposures are generally
offsetting and are recorded in other (income) and expense in the
Consolidated Statement of Earnings. At December 31, 2009,
the total notional amount of derivative instruments in economic
hedges of foreign currency exposure was $13.1 billion.
Equity Risk Management
The company is exposed to market price changes primarily
related to certain obligations to employees. These exposures are
primarily related to market price movements in certain broad
equity market indices and in the company’s own common stock.
Changes in the overall value of these employee compensation
obligations are recorded in SG&A expense in the Consolidated
Statement of Earnings. Although not designated as accounting
hedges, the company utilizes derivatives, including equity swaps
and futures, to economically hedge the exposures related to its
employee compensation obligations. The derivatives are linked
to the total return on certain broad market indices or the total
return on the company’s common stock. They are recorded at
fair value with gains or losses also reported in SG&A expense in
the Consolidated Statement of Earnings. At December 31, 2009,
the total notional amount of derivative instruments in economic
hedges of these compensation obligations was $0.8 billion.
Other Risks
The company holds warrants to purchase shares of common
stock in connection with various investments that are deemed
derivatives because they contain net share or net cash settle-
ment provisions. The amount of shares to be purchased under
these agreements was immaterial at December 31, 2009. The
company records the changes in the fair value of these warrants
in other (income) and expense in the Consolidated Statement
of Earnings.
The company is exposed to a potential loss if a client fails to
pay amounts due under contractual terms. The company utilizes
credit default swaps to economically hedge its credit exposures.
These derivatives have terms of one year or less. The swaps are
recorded at fair value with gains and losses reported in other
(income) and expense in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
The company did not have any derivative instruments relating to
this program outstanding at December 31, 2009.
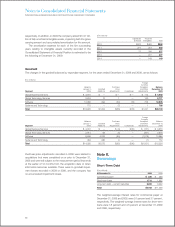
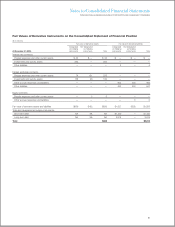
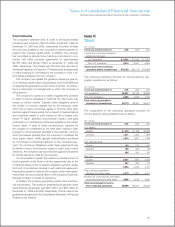
The following tables provide a quantitative summary of the
derivative and non-derivative instrument related risk management
activity as of and for the 12 months ended December 31, 2009:
94