IBM 2009 Annual Report Download - page 79
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 79 of the 2009 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARY COMPANIES
(net investment hedge) in a foreign operation. In addition, the
company may enter into derivative contracts that economically
hedge certain of its risks, even though hedge accounting does
not apply or the company elects not to apply hedge account-
ing. In these cases, there exists a natural hedging relationship
in which changes in the fair value of the derivative, which are
recognized currently in net income, act as an economic offset to
changes in the fair value of the underlying hedged item(s).
Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is designated as a
fair value hedge, along with offsetting changes in the fair value of
the underlying hedged exposure, are recorded in earnings each
period. For hedges of interest rate risk, the fair value adjustments
are recorded as adjustments to interest expense and cost of
financing in the Consoli dated Statement of Earnings. For hedges
of currency risk associated with recorded financial assets or
liabilities, derivative fair value adjustments are recognized in other
(income) and expense in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is designated as a
cash flow hedge are recorded, net of applicable taxes, in accu-
mulated other comprehensive income/(loss), a component of
equity. When net income is affected by the variability of the under-
lying cash flow, the applicable offsetting amount of the gain or
loss from the derivative that is deferred in equity is released to net
income and reported in interest expense, cost, SG&A expense
or other (income) and expense in the Consolidated Statement of
Earnings based on the nature of the underlying cash flow hedged.
Effectiveness for net investment hedging derivatives is measured
on a spot-to-spot basis. The effective portion of changes in the
fair value of net investment hedging derivatives and other non-
derivative financial instruments designated as net investment
hedges are recorded as foreign currency translation adjustments,
net of applicable taxes, in accumulated other comprehensive
income/(loss) in the Consolidated Statement of Changes in
Equity. Changes in the fair value of the portion of a net investment
hedging derivative excluded from the effectiveness assessment
are recorded in interest expense.
When the underlying hedged item ceases to exist, all changes
in the fair value of the derivative are included in net income each
period until the instrument matures. When the derivative trans-
action ceases to exist, a hedged asset or liability is no longer
adjusted for changes in its fair value except as required under
other relevant accounting standards. Derivatives that are not
designated as hedges, as well as changes in the fair value of
derivatives that do not effectively offset changes in the fair value
of the underlying hedged item throughout the designated hedge
period (collectively, “ineffectiveness”), are recorded in net income
each period and are reported in other (income) and expense.
The company reports cash flows arising from derivative
financial instruments designated as fair value or cash flow
hedges consistent with the classification of cash flows from the
underlying hedged items that these derivatives are hedging.
Accordingly, the cash flows associated with derivatives desig-
nated as fair value or cash flow hedges are classified in cash
flows from operating activities in the Consolidated Statement
of Cash Flows. Cash flows from derivatives designated as net
investment hedges and derivatives that do not qualify as hedges
are reported in investing activities. For currency swaps desig-
nated as hedges of foreign currency denominated debt (included
in the company’s debt risk management program as addressed
in note L, “Derivatives and Hedging Transactions,” on pages 92
through 96), cash flows directly associated with the settlement
of the principal element of these swaps are reported in payments
to settle debt in the cash flow from financing activities section of
the Consolidated State ment of Cash Flows.
Financial Instruments
In determining the fair value of its financial instruments, the
company uses a variety of methods and assumptions that are
based on market conditions and risks existing at each balance
sheet date. Refer to note E,
“Financial Instruments (Excluding
Derivatives),” on pages 87 and 88 for further information.
All
methods of assessing fair value result in a general approximation
of value, and such value may never actually be realized.
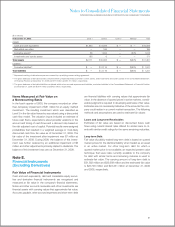
Fair Value Measurement
Exit prices are used to measure assets and liabilities that fall
within the scope of the fair value measurements guidance.
Under this guidance, the company is required to classify certain
assets and liabilities based on the following fair value hierarchy:
• Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets that are unad-
justed and accessible at the measurement date for identical,
unrestricted assets or liabilities;
• Level 2—Quoted prices for identical assets and liabilities in
markets that are not active, quoted prices for similar assets
and liabilities in active markets or financial instruments for
which significant inputs are observable, either directly or
indirectly; and
• Level 3—Prices or valuations that require inputs that are both
significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable.
This guidance requires the use of observable market data if such
data is available without undue cost and effort.
When available, the company uses unadjusted quoted mar-
ket prices to measure the fair value and classifies such items
within Level 1. If quoted market prices are not available, fair
value is based upon internally developed models that use cur-
rent market-based or independently sourced market parameters
such as interest rates and currency rates. Items valued using
internally generated models are classified according to the low-
est level input or value driver that is significant to the valuation.
The determination of fair value considers various factors
including interest rate yield curves and time value underlying the
financial instruments. For derivatives and debt securities, the
company uses a discounted cash flow analysis using discount
rates commensurate with the duration of the instrument. In the
event of an other-than-temporary impairment of a nonpublic
equity method investment, the company uses the net asset
77