Experian 2010 Annual Report Download - page 98
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 98 of the 2010 Experian annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
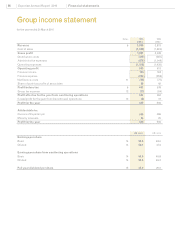
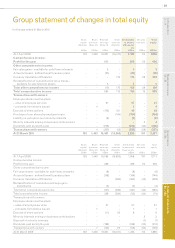
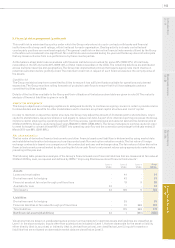
Experian Annual Report 2010 Financial statements96
Notes to the Group nancial statements (continued)
4. Signicant accounting policies (continued)
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash in hand, term and call deposits held with banks and other short-term highly liquid investments
with original maturities of three months or less. Bank overdrafts are shown within borrowings in current liabilities on the Group balance
sheet. For the purposes of the Group cash ow statement, cash and cash equivalents are as dened above, net of bank overdrafts.
Borrowings and borrowing costs
Borrowings are recognised initially at fair value, net of any transaction costs incurred. Borrowings are subsequently stated at
amortised cost except where they are hedged by an effective fair value hedge, in which case the carrying value is adjusted to
reect the fair value movements associated with the hedged risk.
Borrowings are classied as non-current to the extent that the Group has an unconditional right to defer settlement of the
liability for at least one year after the balance sheet date.
Incremental transaction costs which are directly attributable to the issue of debt are capitalised and amortised over the expected life of
the borrowing using the effective interest rate method. All other borrowing costs are expensed in the year in which they are incurred.
Accounting for derivative nancial instruments and hedging activities
The Group uses derivative nancial instruments to manage its exposures to uctuations in foreign exchange rates, interest
rates and certain obligations, including social security obligations, in respect of share-based payments. Derivative instruments
utilised by the Group include interest rate swaps, cross currency swaps, foreign exchange contracts and equity swaps. These are
recognised as assets or liabilities as appropriate.
Derivative nancial instruments are recognised at cost, being the fair value at the date a contract is entered into, and are
subsequently remeasured at their fair value. Depending on the type of the derivative nancial instrument, fair value calculation
techniques include, but are not limited to, quoted market value, present value of estimated future cash ows (of which the
valuation of interest rate swaps is an example) and exchange rates at the balance sheet date (of which the valuation of foreign
exchange contracts is an example). The method of recognising the resulting gain or loss depends on whether the derivative is
designated as a hedging instrument and, if so, the nature of the hedge relationship. The Group designates certain derivatives as:
Fair value hedges - hedges of the fair value of recognised assets or liabilities or a rm commitment; or -
Cash ow hedges - hedges of a particular risk associated with a recognised asset or liability or a highly probable forecast -
transaction; or
Net investment hedges - hedges of net investments in operations whose functional currency is not the US dollar. -
The Group documents the relationship between hedging instruments and hedged items at the hedge inception, as well as its
risk management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge transactions. The Group also documents its assessment,
both at hedge inception and on an ongoing basis, of whether the derivatives that are used in hedging transactions are highly
effective in offsetting changes in fair values of hedged items. This effectiveness testing is performed at every reporting date
throughout the life of the hedge to conrm that the hedge has remained and will continue to remain highly effective.
Hedge accounting is discontinued when the hedging instrument expires or is sold, terminated or exercised or no longer qualies
for hedge accounting.
Derivative assets and liabilities are classied as non-current unless they mature within one year after the balance sheet date.
Amounts payable or receivable in respect of interest rate swaps are taken to net nance costs over the period of the contracts,
together with the interest differentials reected in foreign exchange contracts.
Fair value hedges
Changes in the fair value of derivatives that are designated and qualify as fair value hedging instruments are recorded in the
Group income statement, together with any changes in the fair value of the hedged asset or liability that are attributable to the
hedged risk. The ineffective portion of a fair value hedge is recognised in net nance costs in the Group income statement.
Cash ow hedges
The effective portion of changes in the fair value of derivatives that are designated and qualify as cash ow hedges is
recognised in other comprehensive income. The gain or loss relating to the ineffective portion is recognised immediately within
cost of sales or operating expenses, as appropriate, in the Group income statement.
Amounts accumulated in equity are reclassied in the Group income statement in the period when the hedged item impacts the
Group income statement. However, when the forecast transaction that is hedged results in the recognition of a non-nancial asset
or liability, the gains and losses previously deferred in equity are transferred from equity and included in the initial measurement
of the cost of the asset or liability. When a hedging instrument expires or is sold, or when a hedge no longer meets the criteria for
hedge accounting, any cumulative gain or loss included in equity at that time remains in equity and is recognised when the forecast
transaction is ultimately recognised in the Group income statement. When a forecast transaction is no longer expected to occur, the
cumulative gain or loss that was included in equity is transferred immediately to the Group income statement.